Exhibit 99.2













Transformative immunomodulating medicines for patients January 2026 1

2 Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains “forward-looking
statements” within the meaning of the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Words such as “may”, “will”, “believe”, “expect”, “plan”, “anticipate”, “estimate”, “expect”, “continue” and similar
expressions (as well as other words or expressions referencing future events or circumstances) are intended to identify forward-looking statements. All statements, other than statements of historical facts, included in this presentation are
forward-looking statements. These statements include, but are not limited to, Immunocore’s capabilities across oncology, autoimmune and infectious disease therapeutic areas and its ability to advance its clinical and pre-clinical pipeline;
the estimated market size and patient population for KIMMTRAK and Immunocore’s other product candidates; the growth opportunities for KIMMTRAK, including HLA-A02+ melanoma, cutaneous melanoma and adjuvant uveal melanoma; expected submission
of investigational new drug applications or clinical trial applications; the potential regulatory approval, expected clinical benefits and availability of Immunocore’s product candidates; the commercial performance of KIMMTRAK, including
Immunocore’s expectations of moderate revenue growth in 2026; the potential benefits and advantages that KIMMTRAK, brenetafusp and Immunocore’s other product candidates will provide for patients, alone or in combination with other
therapies; expectations regarding the design, progress, timing, enrollment, scope, expansion, funding, and results of Immunocore’s existing and planned clinical trials, those of Immunocore’s collaboration partners or the combined clinical
trials with Immunocore’s collaboration partners; the timing and sufficiency of clinical trial outcomes to support potential approval of any of Immunocore’s product candidates or those of, or combined with, its collaboration partners;
expected commercial and clinical milestones and Immunocore’s ability to achieve those milestones on their expected timeline, or at all; the value of Immunocore’s products and product candidates for patients and shareholders; Immunocore’s
strategic priorities for 2026 and potential growth opportunities and trends, including in connection with product launches; and the preliminary unaudited cash position of Immunocore as of December 31, 2025. Any forward-looking statements
are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs of future events and are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that could cause actual events or results to differ materially and adversely from those set forth in or
implied by such forward-looking statements, many of which are beyond Immunocore’s control. These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, the impact of worsening macroeconomic conditions on Immunocore’s business, financial
position, strategy and anticipated milestones, including Immunocore’s ability to conduct ongoing and planned clinical trials; Immunocore’s ability to obtain a clinical supply of current or future product candidates or commercial supply of
KIMMTRAK or any future approved products; Immunocore’s ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval of its product candidates, including KIMMTRAK; Immunocore’s ability and plans in continuing to establish and expand a commercial
infrastructure and to successfully launch, market and sell KIMMTRAK and any future approved products; Immunocore’s ability to successfully expand the approved indications for KIMMTRAK or obtain marketing approval for KIMMTRAK in additional
geographies in the future; the delay of any current or planned clinical trials, whether due to patient enrollment delays or otherwise; Immunocore’s ability to successfully demonstrate the safety and efficacy of its product candidates and
gain approval of its product candidates on a timely basis, if at all; competition with respect to market opportunities; unexpected safety or efficacy data observed during preclinical studies or clinical trials; actions of regulatory
agencies, which may affect the initiation, timing and progress of clinical trials or future regulatory approval; Immunocore’s need for and ability to obtain additional funding, on favorable terms or at all, including as a result of
worsening macroeconomic conditions, including changes inflation and interest rates and unfavorable general market conditions, and the impacts thereon of the war in Ukraine, the conflict in the Middle East, and global geopolitical tension;
Immunocore’s ability to obtain, maintain and enforce intellectual property protection for KIMMTRAK or any product candidates it or its collaborators are developing; and the success of Immunocore’s current and future collaborations,
partnerships or licensing arrangements. These and other risks and uncertainties are described in greater detail in the section titled "Risk Factors" in Immunocore’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including Immunocore’s
most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 26, 2025, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties, and other important factors in
Immunocore’s subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. All forward-looking statements contained in this presentation speak only as of the date on which they were made and should not be relied upon as representing its
views as of any subsequent date. Except to the extent required by law, Immunocore undertakes no obligation to update such statements to reflect events that occur or circumstances that exist after the date on which they were made. In
addition, as the reported cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities in this presentation are preliminary, have not been audited and are subject to change pending completion of Immunocore’s audited financial statements for the year
ended December 31, 2025, it is possible that Immunocore or its independent registered public accounting firm may identify items that require Immunocore to make adjustments to the amount included in this release, and such changes could be
material. Additional information and disclosures would also be required for a more complete understanding of Immunocore’s financial position and results of operations as of December 31, 2025. Certain information contained in this
presentation relates to or is based on studies, publications, surveys, and other data obtained from third party sources and Immunocore’s own internal estimates and research. While Immunocore believes these third party sources to be reliable
as of the date of this presentation, it has not independently verified, and makes no representation as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy, or completeness of, any information obtained from third party sources. KIMMTRAK is a trademark
owned or licensed to Immunocore.

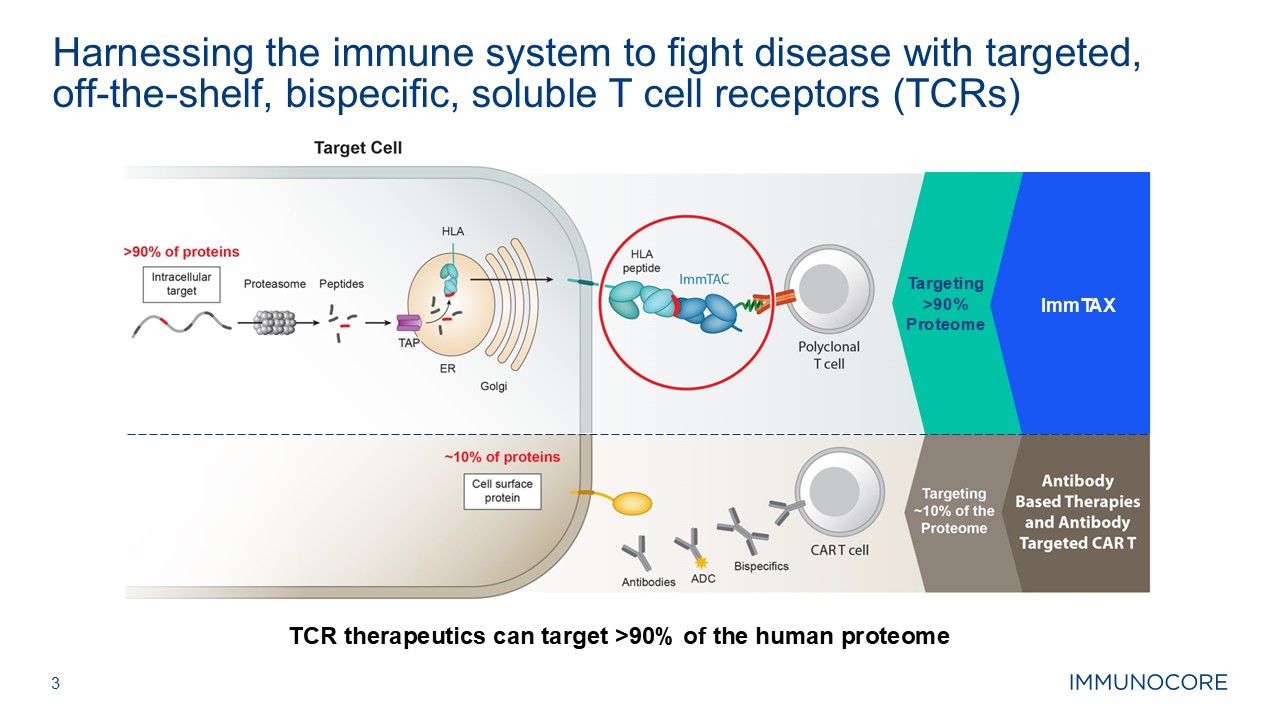
3 Harnessing the immune system to fight disease with targeted, off-the-shelf,
bispecific, soluble T cell receptors (TCRs) TCR therapeutics can target >90% of the human proteome ImmTAX Targeting >90% Proteome

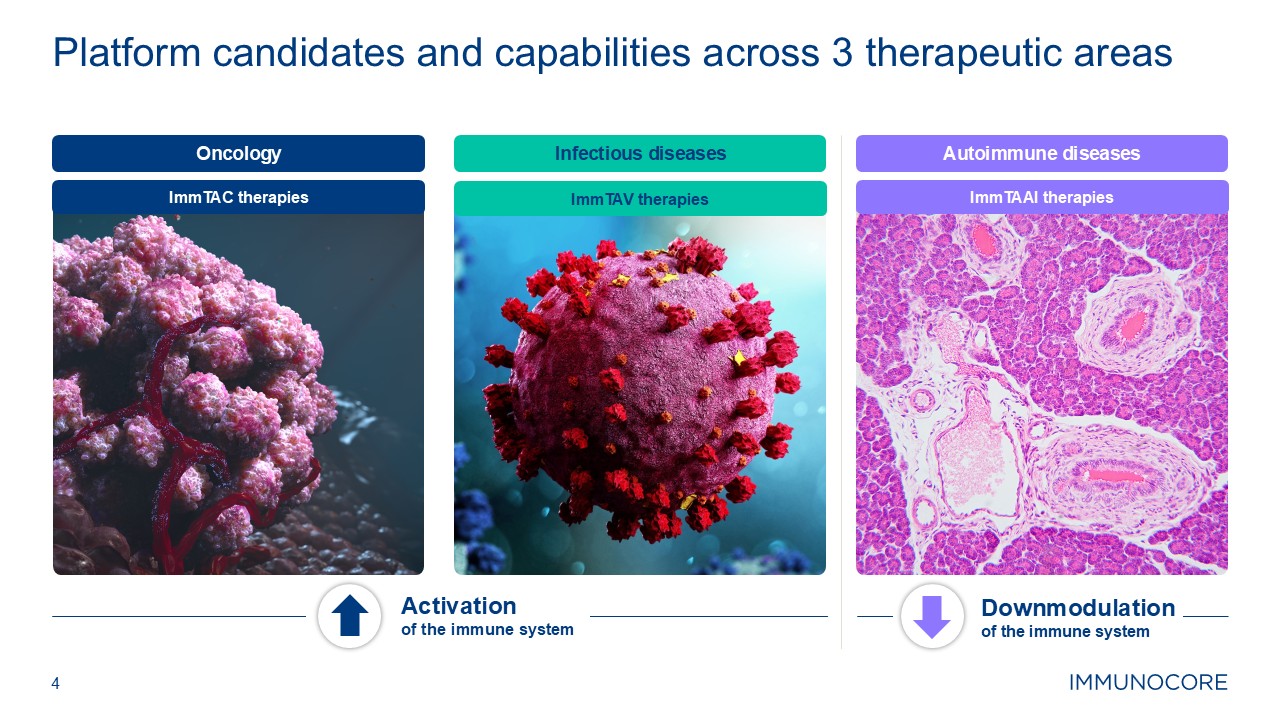
4 Platform candidates and capabilities across 3 therapeutic areas Activation
of the immune system Downmodulation of the immune system Infectious diseases Autoimmune diseases ImmTAC therapies ImmTAV therapies ImmTAAI therapies Oncology

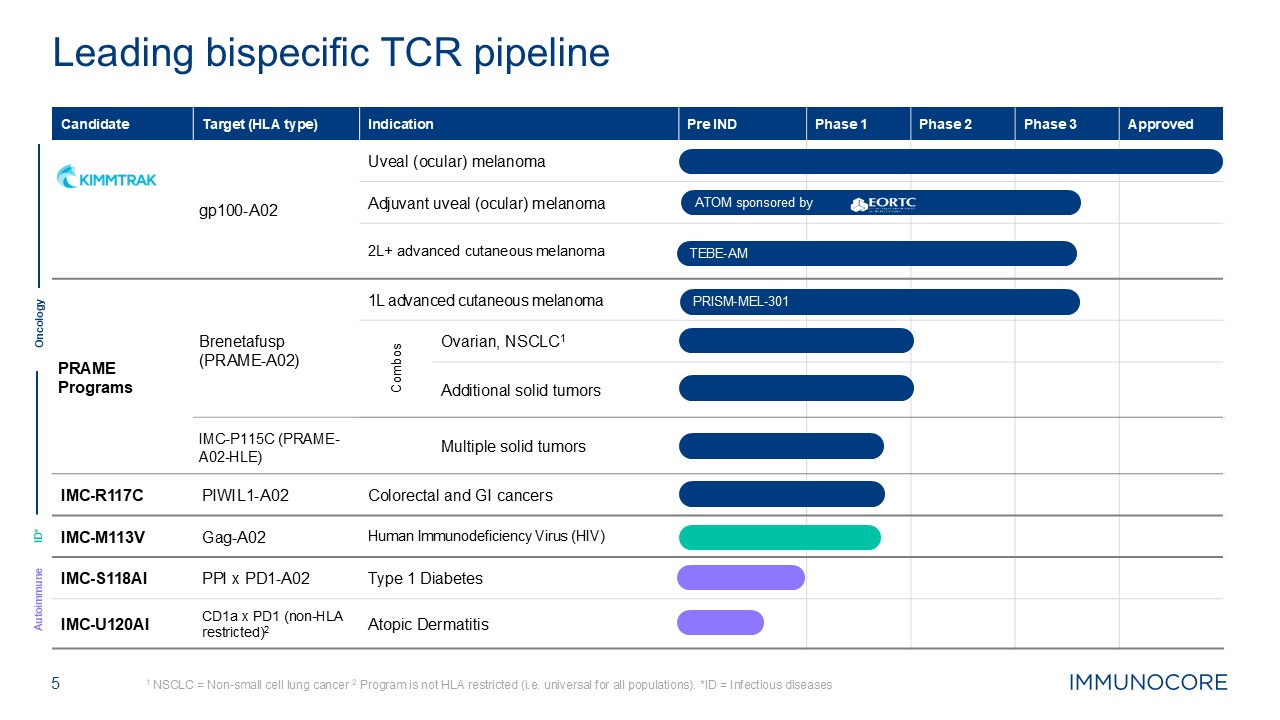
1 NSCLC = Non-small cell lung cancer 2 Program is not HLA restricted (i.e.
universal for all populations). *ID = Infectious diseases Leading bispecific TCR pipeline Candidate Target (HLA type) Indication Pre IND Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Approved gp100-A02 Uveal (ocular) melanoma Adjuvant uveal (ocular)
melanoma 2L+ advanced cutaneous melanoma PRAME Programs Brenetafusp (PRAME-A02) 1L advanced cutaneous melanoma Combos Ovarian, NSCLC1 Additional solid tumors IMC-P115C (PRAME-A02-HLE) Multiple solid
tumors IMC-R117C PIWIL1-A02 Colorectal and GI cancers IMC-M113V Gag-A02 Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) IMC-S118AI PPI x PD1-A02 Type 1 Diabetes IMC-U120AI CD1a x PD1 (non-HLA restricted)2 Atopic Dermatitis
Oncology ID* Autoimmune 5 TEBE-AM PRISM-MEL-301 ATOM sponsored by

Maximizing potential of KIMMTRAK® in HLA‑A02+ melanoma 6

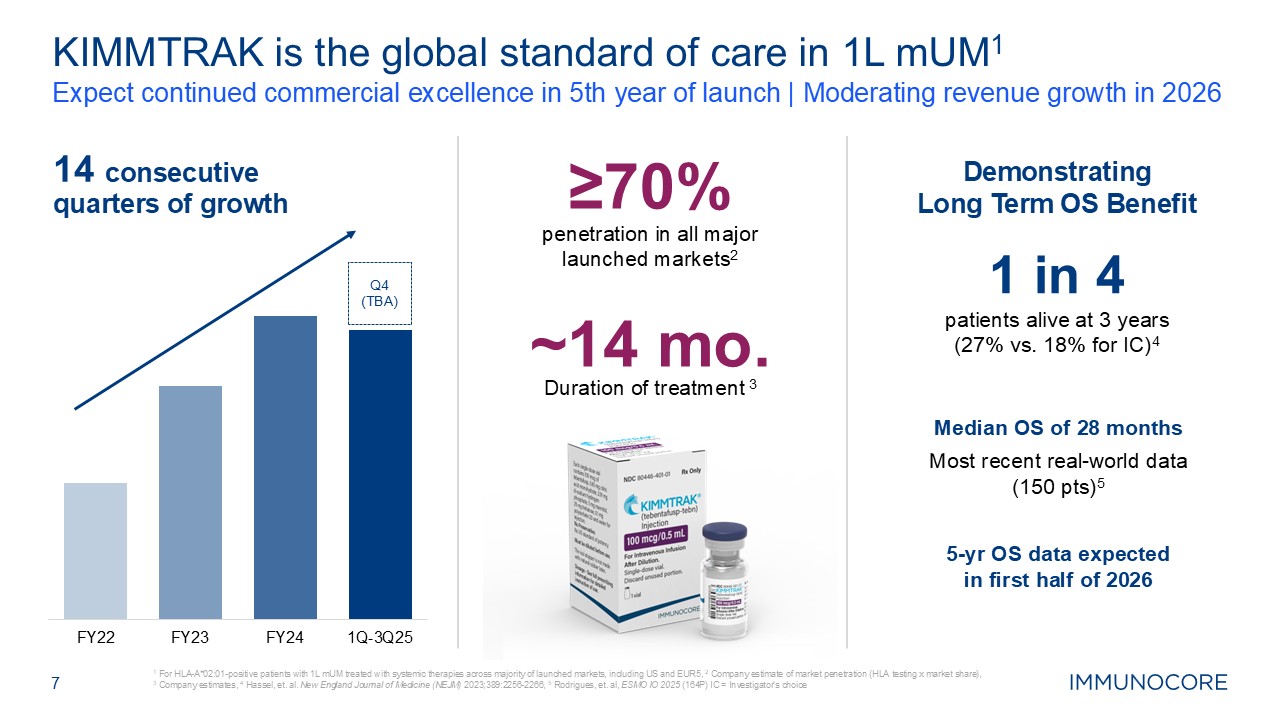
7 Expect continued commercial excellence in 5th year of launch | Moderating
revenue growth in 2026 1 For HLA-A*02:01-positive patients with 1L mUM treated with systemic therapies across majority of launched markets, including US and EUR5, 2 Company estimate of market penetration (HLA testing x market share), 3
Company estimates, 4 Hassel, et. al. New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) 2023;389:2256-2266, 5 Rodrigues, et. al, ESMO IO 2025 (164P) IC = Investigator’s choice KIMMTRAK is the global standard of care in 1L mUM1 14 consecutive quarters
of growth penetration in all major launched markets2 ≥70% Duration of treatment 3 ~14 mo. patients alive at 3 years (27% vs. 18% for IC)4 1 in 4 Q4 (TBA) Demonstrating Long Term OS Benefit Median OS of 28 months Most recent
real-world data (150 pts)5 5-yr OS data expected in first half of 2026

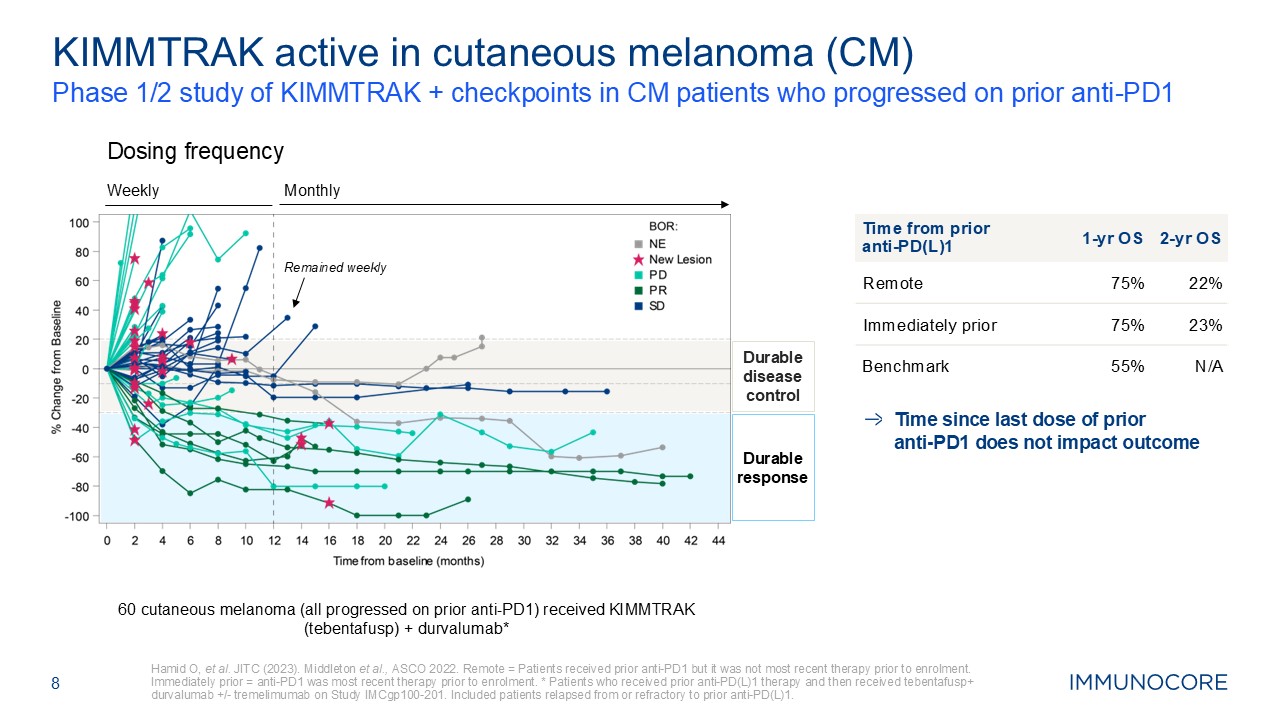
8 Phase 1/2 study of KIMMTRAK + checkpoints in CM patients who progressed on
prior anti-PD1 Hamid O, et al. JITC (2023). Middleton et al., ASCO 2022. Remote = Patients received prior anti-PD1 but it was not most recent therapy prior to enrolment. Immediately prior = anti-PD1 was most recent therapy prior to
enrolment. * Patients who received prior anti-PD(L)1 therapy and then received tebentafusp+ durvalumab +/- tremelimumab on Study IMCgp100-201. Included patients relapsed from or refractory to prior anti-PD(L)1. KIMMTRAK active in cutaneous
melanoma (CM) Time from prior anti‑PD(L)1 1-yr OS 2-yr OS Remote 75% 22% Immediately prior 75% 23% Benchmark 55% N/A Weekly Monthly Dosing frequency Remained weekly Durable response Durable disease control 60
cutaneous melanoma (all progressed on prior anti-PD1) received KIMMTRAK (tebentafusp) + durvalumab* Time since last dose of prior anti‑PD1 does not impact outcome

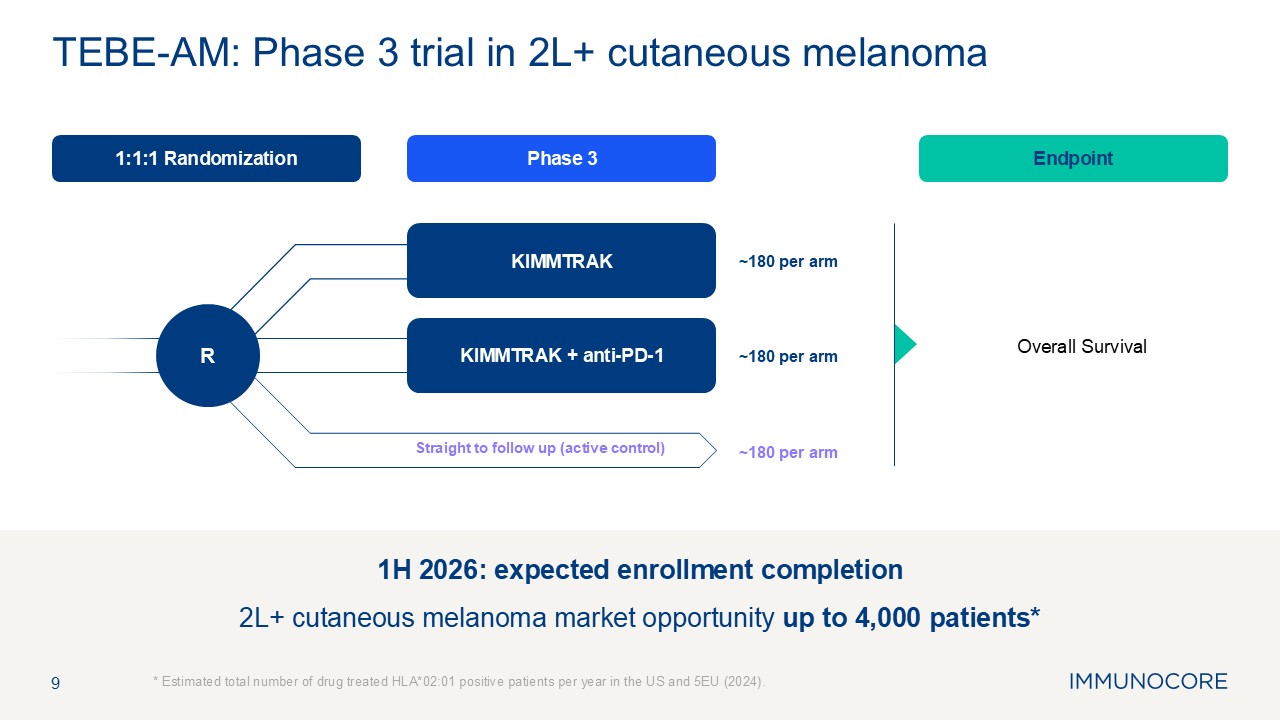
9 * Estimated total number of drug treated HLA*02:01 positive patients per
year in the US and 5EU (2024). TEBE-AM: Phase 3 trial in 2L+ cutaneous melanoma Phase 3 Endpoint 1:1:1 Randomization Overall Survival KIMMTRAK KIMMTRAK + anti-PD-1 Straight to follow up (active control) R ~180 per arm ~180 per
arm ~180 per arm 1H 2026: expected enrollment completion 2L+ cutaneous melanoma market opportunity up to 4,000 patients*

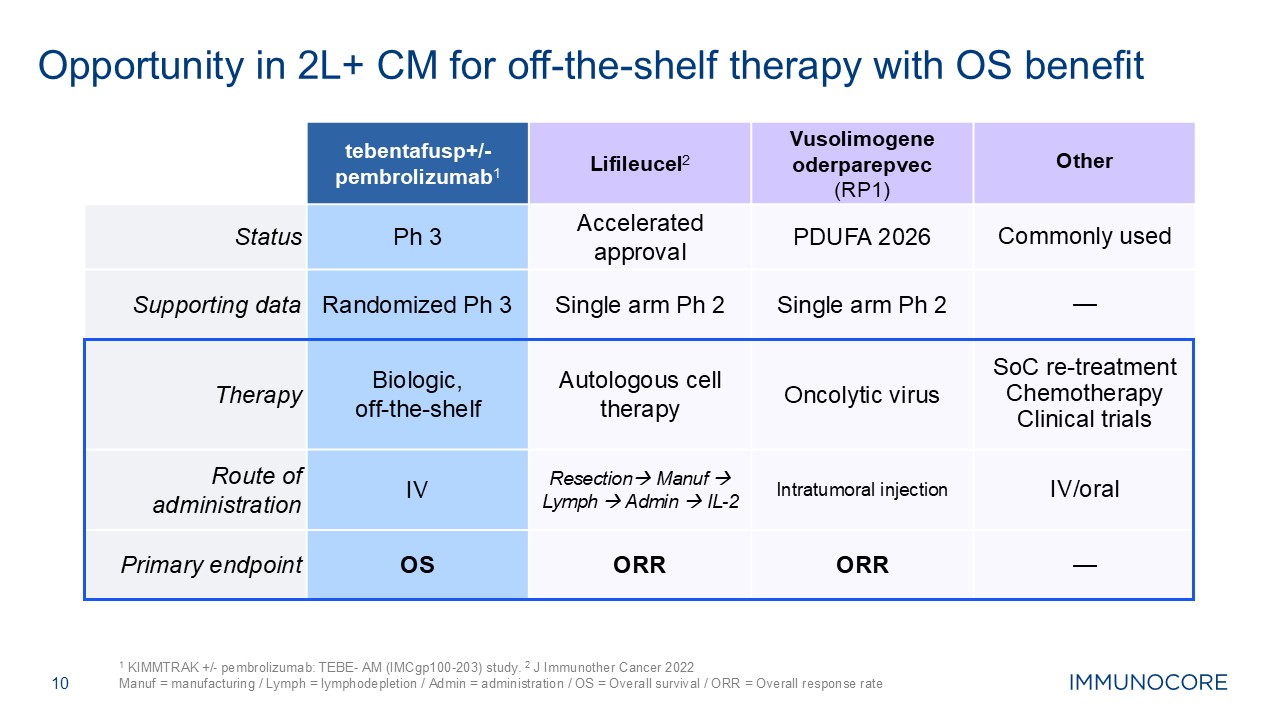
10 1 KIMMTRAK +/- pembrolizumab: TEBE- AM (IMCgp100-203) study. 2 J
Immunother Cancer 2022 Manuf = manufacturing / Lymph = lymphodepletion / Admin = administration / OS = Overall survival / ORR = Overall response rate tebentafusp+/- pembrolizumab1 Lifileucel2 Vusolimogene
oderparepvec (RP1) Other Status Ph 3 Accelerated approval PDUFA 2026 Commonly used Supporting data Randomized Ph 3 Single arm Ph 2 Single arm Ph 2 — Therapy Biologic, off-the-shelf Autologous cell therapy Oncolytic
virus SoC re-treatment Chemotherapy Clinical trials Route of administration IV Resection Manuf Lymph Admin IL-2 Intratumoral injection IV/oral Primary endpoint OS ORR ORR — Opportunity in 2L+ CM for off-the-shelf therapy
with OS benefit

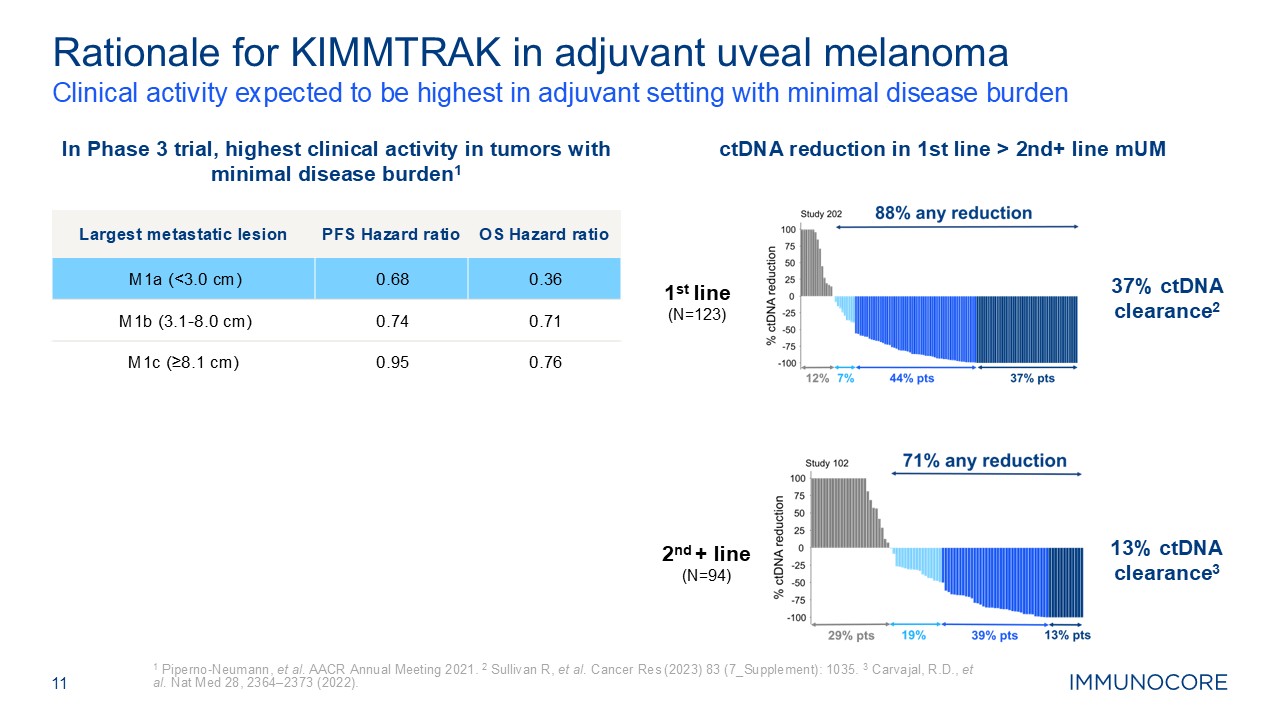
Clinical activity expected to be highest in adjuvant setting with minimal
disease burden 1 Piperno-Neumann, et al. AACR Annual Meeting 2021. 2 Sullivan R, et al. Cancer Res (2023) 83 (7_Supplement): 1035. 3 Carvajal, R.D., et al. Nat Med 28, 2364–2373 (2022). 11 Rationale for KIMMTRAK in adjuvant uveal
melanoma In Phase 3 trial, highest clinical activity in tumors with minimal disease burden1 ctDNA reduction in 1st line > 2nd+ line mUM 1st line (N=123) 37% ctDNA clearance2 2nd + line (N=94) 13% ctDNA clearance3 Largest
metastatic lesion PFS Hazard ratio OS Hazard ratio M1a (<3.0 cm) 0.68 0.36 M1b (3.1-8.0 cm) 0.74 0.71 M1c (≥8.1 cm) 0.95 0.76

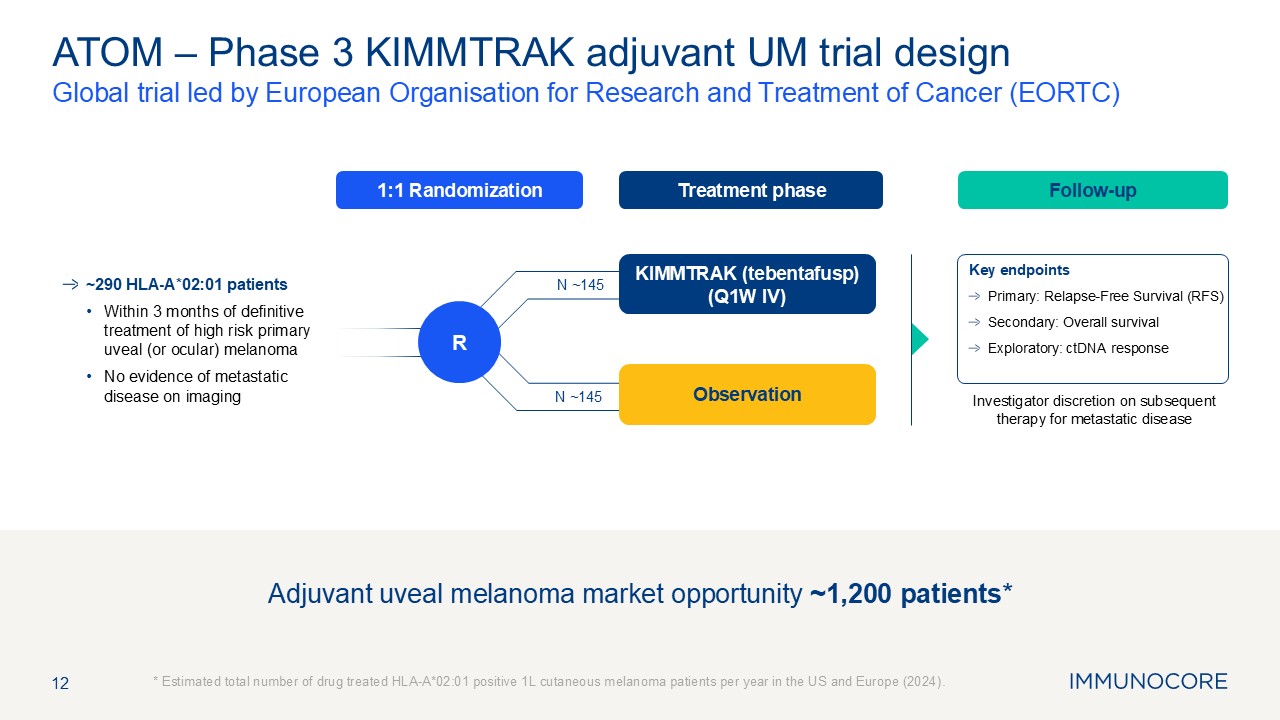
Treatment phase Follow-up 1:1 Randomization 12 Global trial led by
European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) * Estimated total number of drug treated HLA-A*02:01 positive 1L cutaneous melanoma patients per year in the US and Europe (2024). ATOM – Phase 3 KIMMTRAK adjuvant UM
trial design Investigator discretion on subsequent therapy for metastatic disease KIMMTRAK (tebentafusp) (Q1W IV) R ~290 HLA-A*02:01 patients Within 3 months of definitive treatment of high risk primary uveal (or ocular) melanoma No
evidence of metastatic disease on imaging Key endpoints Primary: Relapse-Free Survival (RFS) Secondary: Overall survival Exploratory: ctDNA response Observation Adjuvant uveal melanoma market opportunity ~1,200 patients* N ~145 N
~145

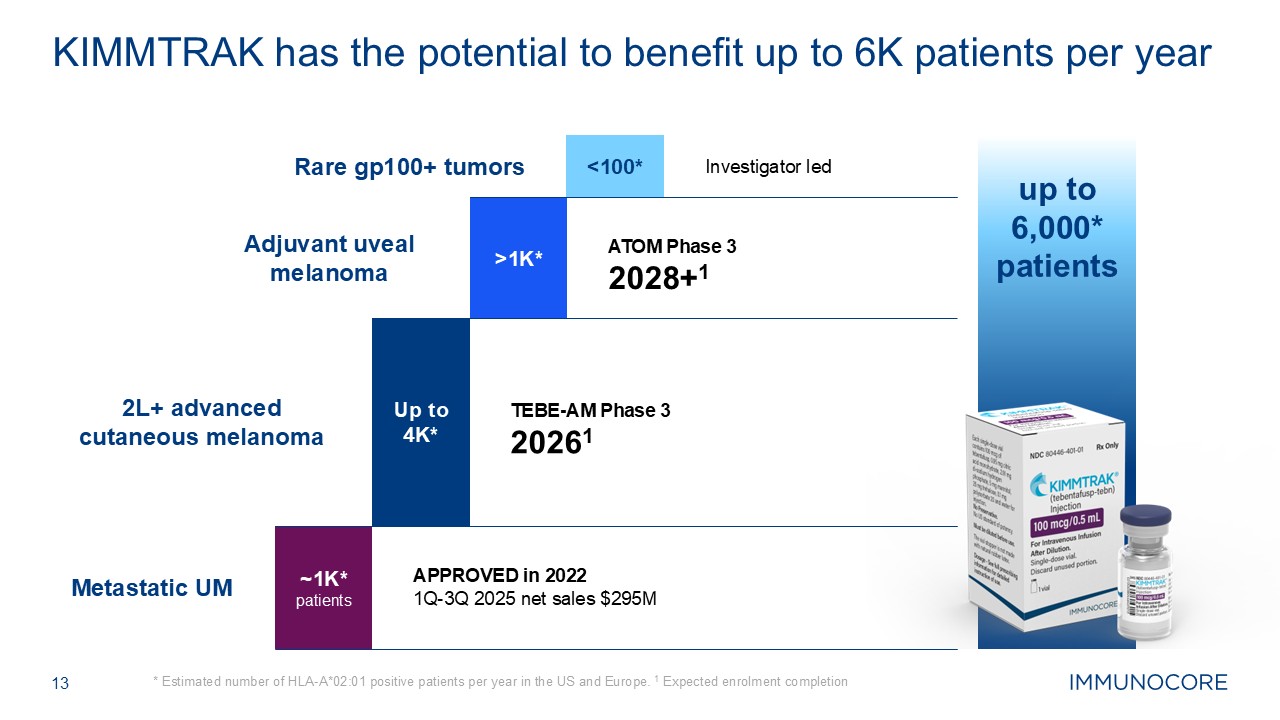
up to 6,000* patients 13 * Estimated number of HLA-A*02:01 positive patients
per year in the US and Europe. 1 Expected enrolment completion KIMMTRAK has the potential to benefit up to 6K patients per year ~1K* patients Up to 4K* >1K* 2L+ advanced cutaneous melanoma <100* APPROVED in 2022 1Q-3Q 2025 net
sales $295M TEBE-AM Phase 3 20261 ATOM Phase 3 2028+1 Investigator led Adjuvant uveal melanoma Rare gp100+ tumors Metastatic UM

PRAME portfolio 14

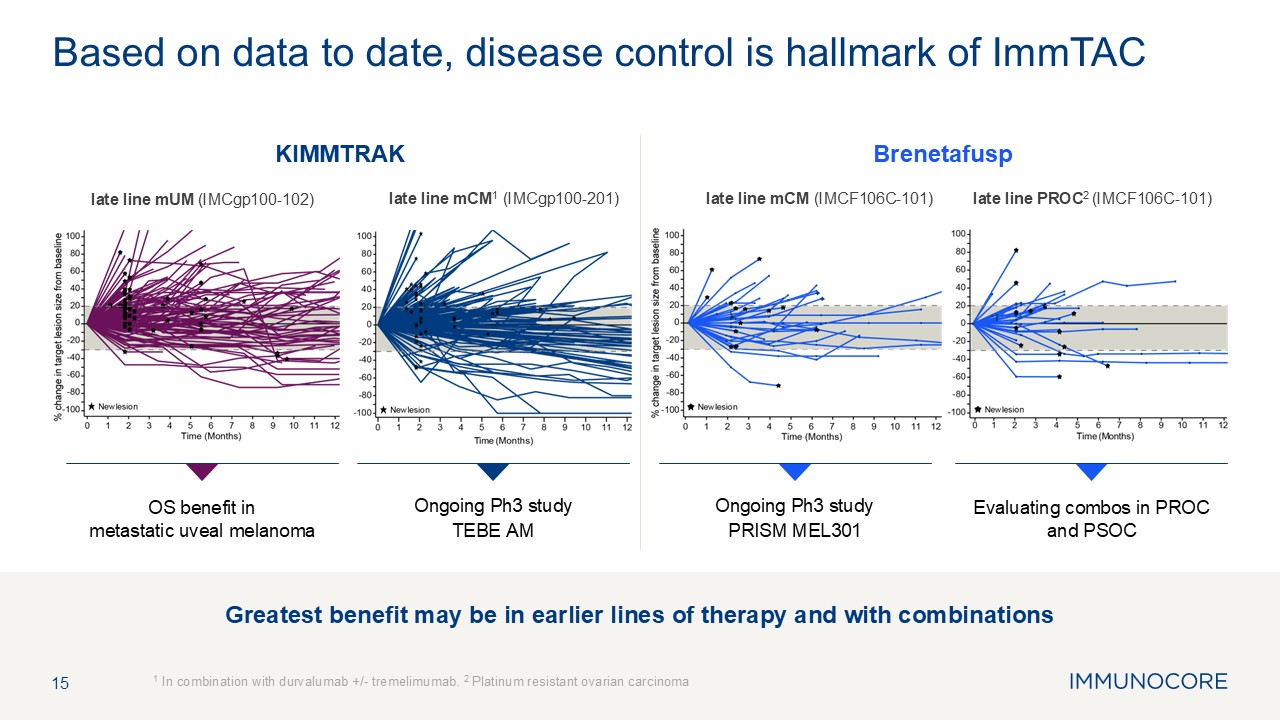
Greatest benefit may be in earlier lines of therapy and with
combinations 15 1 In combination with durvalumab +/- tremelimumab. 2 Platinum resistant ovarian carcinoma Based on data to date, disease control is hallmark of ImmTAC Ongoing Ph3 study PRISM MEL301 Evaluating combos in PROC and
PSOC Brenetafusp late line mUM (IMCgp100-102) OS benefit inmetastatic uveal melanoma Ongoing Ph3 study TEBE AM KIMMTRAK late line mCM1 (IMCgp100-201) late line mCM (IMCF106C-101) late line PROC2 (IMCF106C-101)

Brenetafusp in cutaneous melanoma 16

17 Includes patients receiving target doses ≥20mcg. 1 CRS graded per ASTCT
2019 criteria; all other AE per CTCAE v5.0. 2 Rash is a composite term for a list of skin toxicities of any grade (Nathan et al. 2021). Other G3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAE, in 1 pt each): anemia, chronic inflammatory
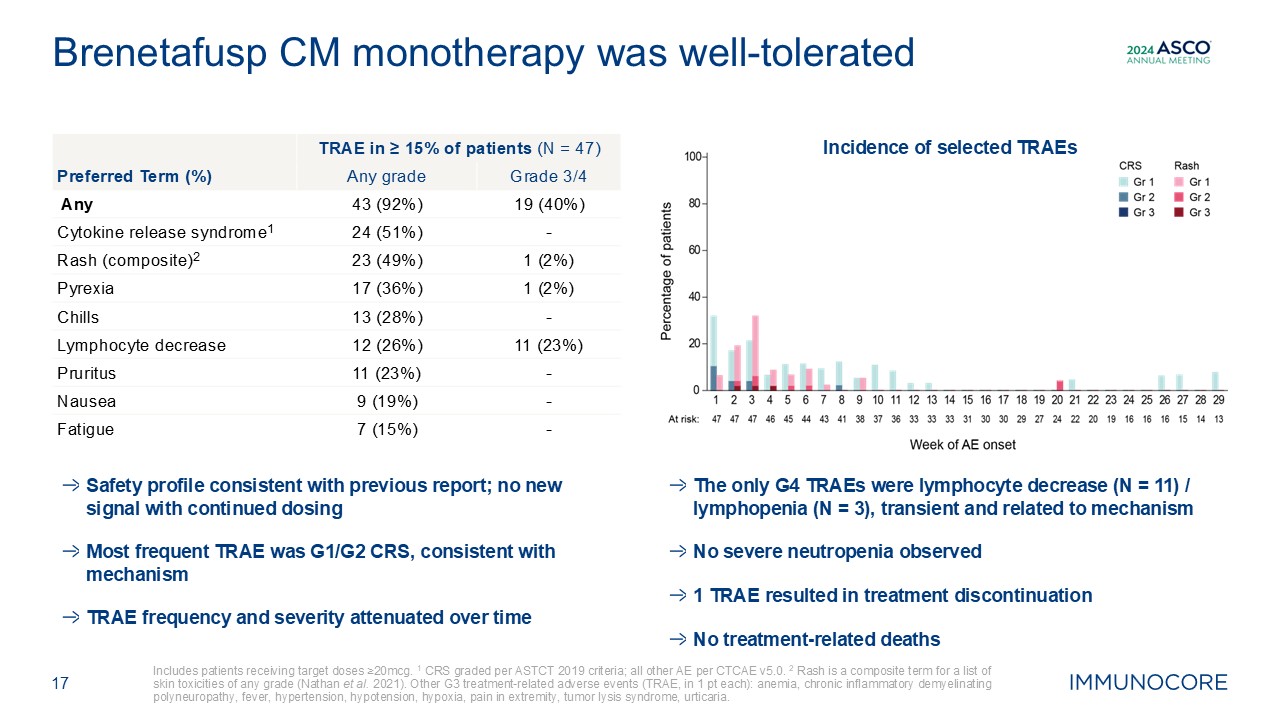
demyelinating polyneuropathy, fever, hypertension, hypotension, hypoxia, pain in extremity, tumor lysis syndrome, urticaria. Brenetafusp CM monotherapy was well-tolerated Incidence of selected TRAEs Safety profile consistent with
previous report; no new signal with continued dosing Most frequent TRAE was G1/G2 CRS, consistent with mechanism TRAE frequency and severity attenuated over time The only G4 TRAEs were lymphocyte decrease (N = 11) / lymphopenia (N = 3),
transient and related to mechanism No severe neutropenia observed 1 TRAE resulted in treatment discontinuation No treatment-related deaths TRAE in ≥ 15% of patients (N = 47) Preferred Term (%) Any grade Grade 3/4 Any 43 (92%) 19
(40%) Cytokine release syndrome1 24 (51%) - Rash (composite)2 23 (49%) 1 (2%) Pyrexia 17 (36%) 1 (2%) Chills 13 (28%) - Lymphocyte decrease 12 (26%) 11 (23%) Pruritus 11 (23%) - Nausea 9 (19%) - Fatigue 7 (15%) -

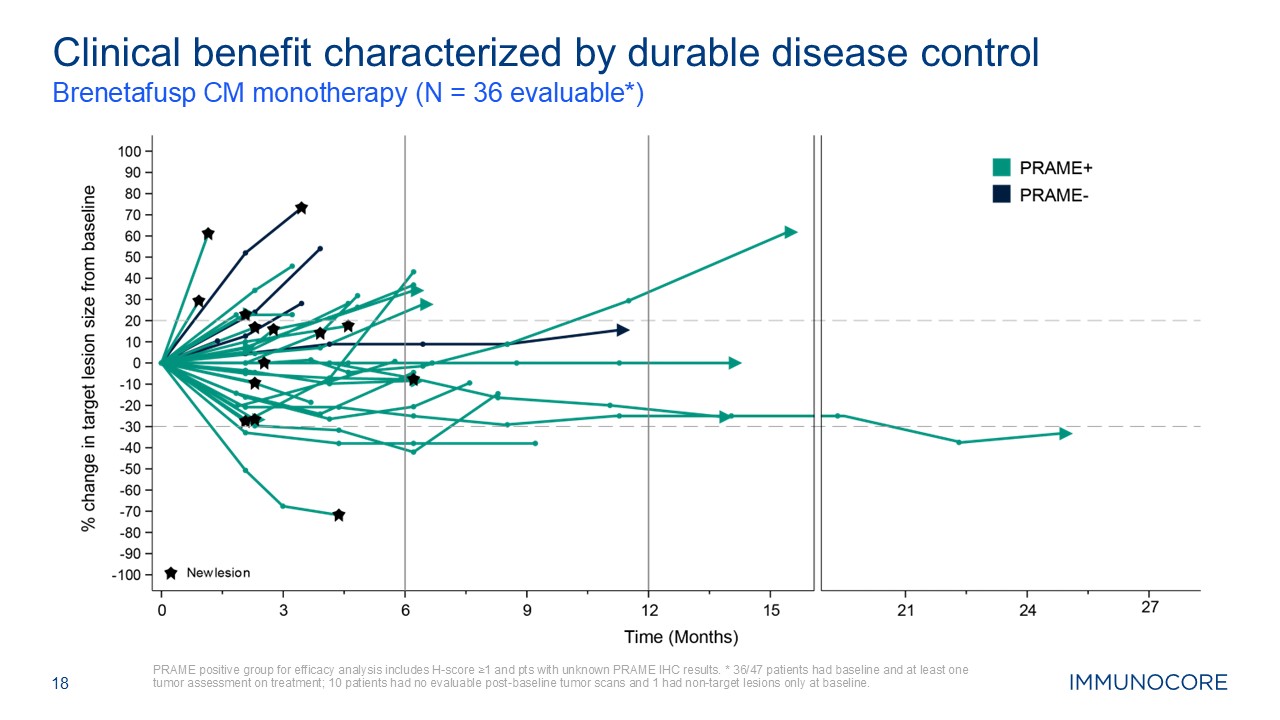
18 Brenetafusp CM monotherapy (N = 36 evaluable*) PRAME positive group for
efficacy analysis includes H-score ≥1 and pts with unknown PRAME IHC results. * 36/47 patients had baseline and at least one tumor assessment on treatment; 10 patients had no evaluable post-baseline tumor scans and 1 had non-target lesions
only at baseline. Clinical benefit characterized by durable disease control

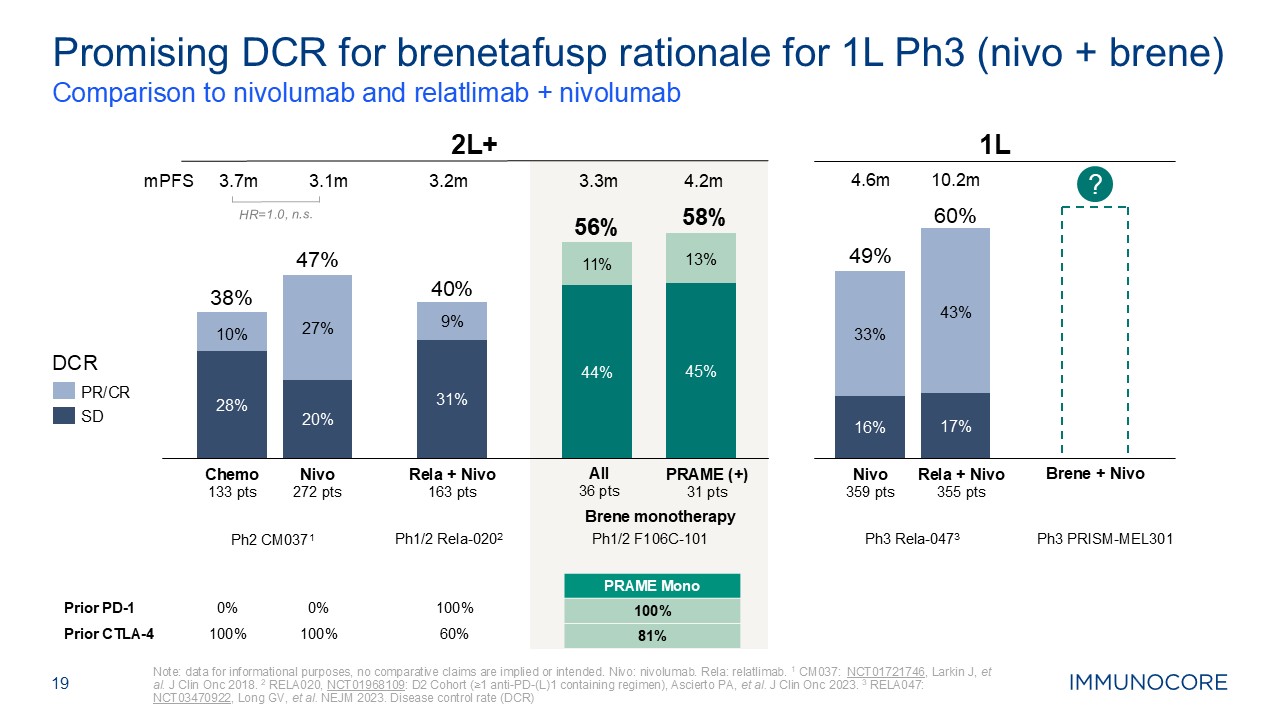
19 Comparison to nivolumab and relatlimab + nivolumab Note: data for
informational purposes, no comparative claims are implied or intended. Nivo: nivolumab. Rela: relatlimab. 1 CM037: NCT01721746, Larkin J, et al. J Clin Onc 2018. 2 RELA020, NCT01968109: D2 Cohort (≥1 anti-PD-(L)1 containing regimen),
Ascierto PA, et al. J Clin Onc 2023. 3 RELA047: NCT03470922, Long GV, et al. NEJM 2023. Disease control rate (DCR) Promising DCR for brenetafusp rationale for 1L Ph3 (nivo + brene) Prior PD-1 0% 0% 100% Prior
CTLA-4 100% 100% 60% Ph1/2 Rela-0202 Ph1/2 F106C-101 PRAME Mono 100% 81% All 36 pts PRAME (+) 31 pts 2L+ PR/CR SD DCR Nivo 272 pts Rela + Nivo 163
pts 8% 28% 27% 20% 31% 9% 38% 47% 40% 11% 44% 13% 45% 56% 58% Chemo 133 pts Ph2 CM0371 27% 20% 9% 31% 11% 44% 13% 45% HR=1.0, n.s. mPFS 3.7m 3.1m 3.2m 3.3m 4.2m 1L Rela + Nivo 355 pts 49% 60% Nivo 359
pts Ph3 Rela-0473 Ph3 PRISM-MEL301 ? Brene + Nivo 33% 16% 43% 17% 4.6m 10.2m Brene monotherapy 10% 28%

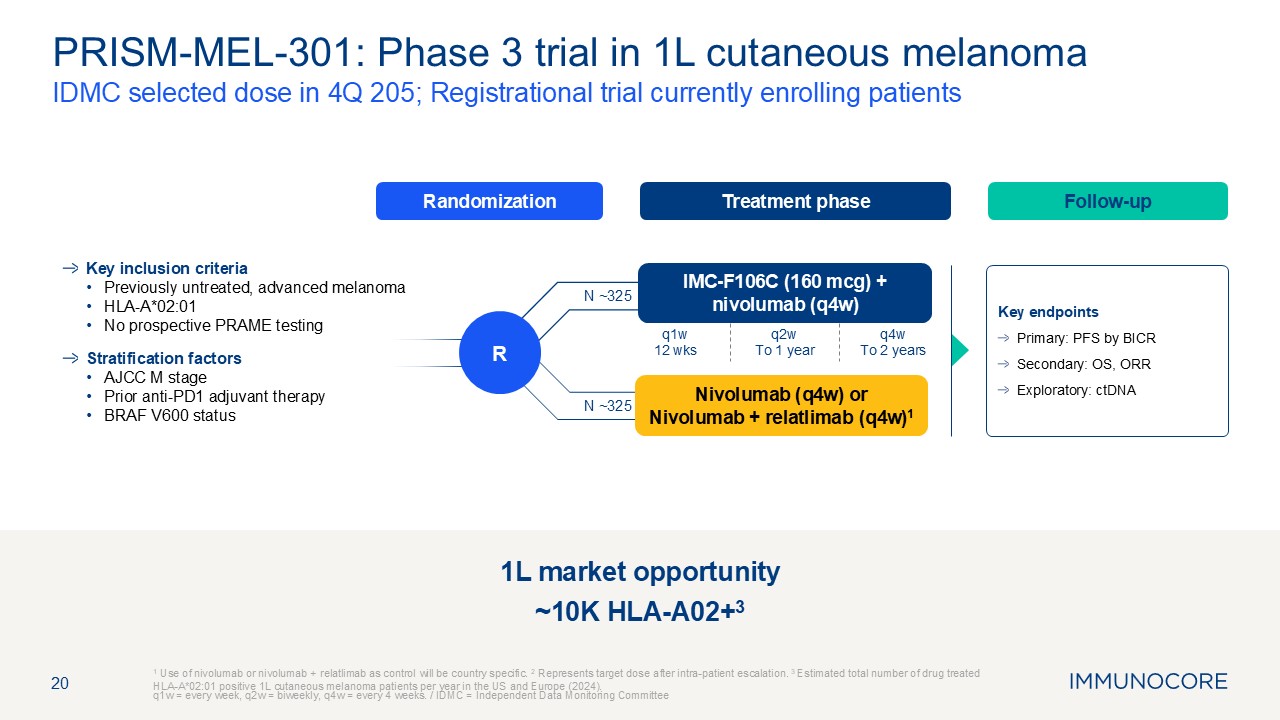
20 IDMC selected dose in 4Q 205; Registrational trial currently enrolling
patients 1 Use of nivolumab or nivolumab + relatlimab as control will be country specific. 2 Represents target dose after intra-patient escalation. 3 Estimated total number of drug treated HLA-A*02:01 positive 1L cutaneous melanoma
patients per year in the US and Europe (2024). q1w = every week, q2w = biweekly, q4w = every 4 weeks. / IDMC = Independent Data Monitoring Committee PRISM-MEL-301: Phase 3 trial in 1L cutaneous melanoma Treatment
phase Follow-up Randomization R Key inclusion criteria Previously untreated, advanced melanoma HLA-A*02:01 No prospective PRAME testing Stratification factors AJCC M stage Prior anti-PD1 adjuvant therapy BRAF V600 status Key
endpoints Primary: PFS by BICR Secondary: OS, ORR Exploratory: ctDNA IMC-F106C (160 mcg) + nivolumab (q4w) Nivolumab (q4w) or Nivolumab + relatlimab (q4w)1 N ~325 N ~325 q1w 12 wks q2w To 1 year q4w To 2 years 1L market
opportunity ~10K HLA-A02+3

Brenetafusp in ovarian 21

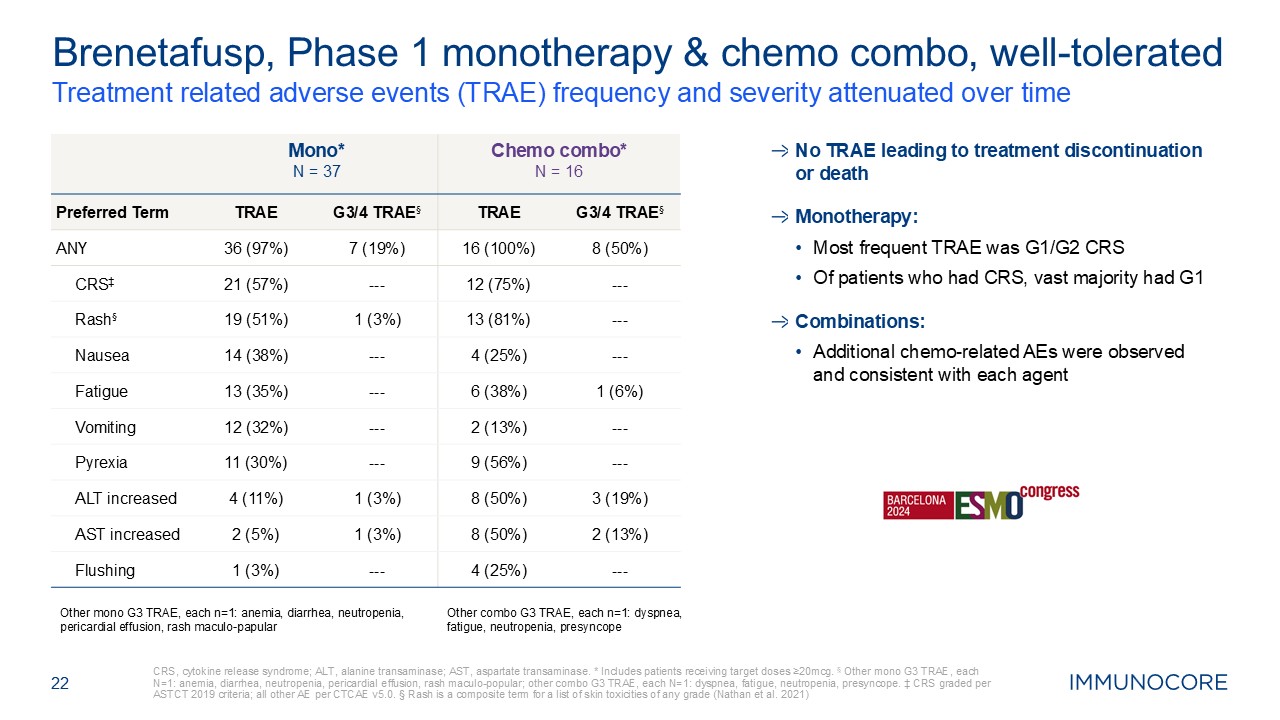
22 Treatment related adverse events (TRAE) frequency and severity attenuated
over time CRS, cytokine release syndrome; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase. * Includes patients receiving target doses ≥20mcg. § Other mono G3 TRAE, each N=1: anemia, diarrhea, neutropenia, pericardial effusion, rash
maculo-popular; other combo G3 TRAE, each N=1: dyspnea, fatigue, neutropenia, presyncope. ‡ CRS graded per ASTCT 2019 criteria; all other AE per CTCAE v5.0. § Rash is a composite term for a list of skin toxicities of any grade (Nathan et
al. 2021) Brenetafusp, Phase 1 monotherapy & chemo combo, well-tolerated Mono* N = 37 Chemo combo* N = 16 Preferred Term TRAE G3/4 TRAE§ TRAE G3/4 TRAE§ ANY 36 (97%) 7 (19%) 16 (100%) 8 (50%) CRS‡ 21 (57%) --- 12
(75%) --- Rash§ 19 (51%) 1 (3%) 13 (81%) --- Nausea 14 (38%) --- 4 (25%) --- Fatigue 13 (35%) --- 6 (38%) 1 (6%) Vomiting 12 (32%) --- 2 (13%) --- Pyrexia 11 (30%) --- 9 (56%) --- ALT increased 4 (11%) 1 (3%) 8
(50%) 3 (19%) AST increased 2 (5%) 1 (3%) 8 (50%) 2 (13%) Flushing 1 (3%) --- 4 (25%) --- Other mono G3 TRAE, each n=1: anemia, diarrhea, neutropenia, pericardial effusion, rash maculo-papular Other combo G3 TRAE, each n=1:
dyspnea, fatigue, neutropenia, presyncope No TRAE leading to treatment discontinuation or death Monotherapy: Most frequent TRAE was G1/G2 CRS Of patients who had CRS, vast majority had G1 Combinations: Additional chemo-related AEs
were observed and consistent with each agent

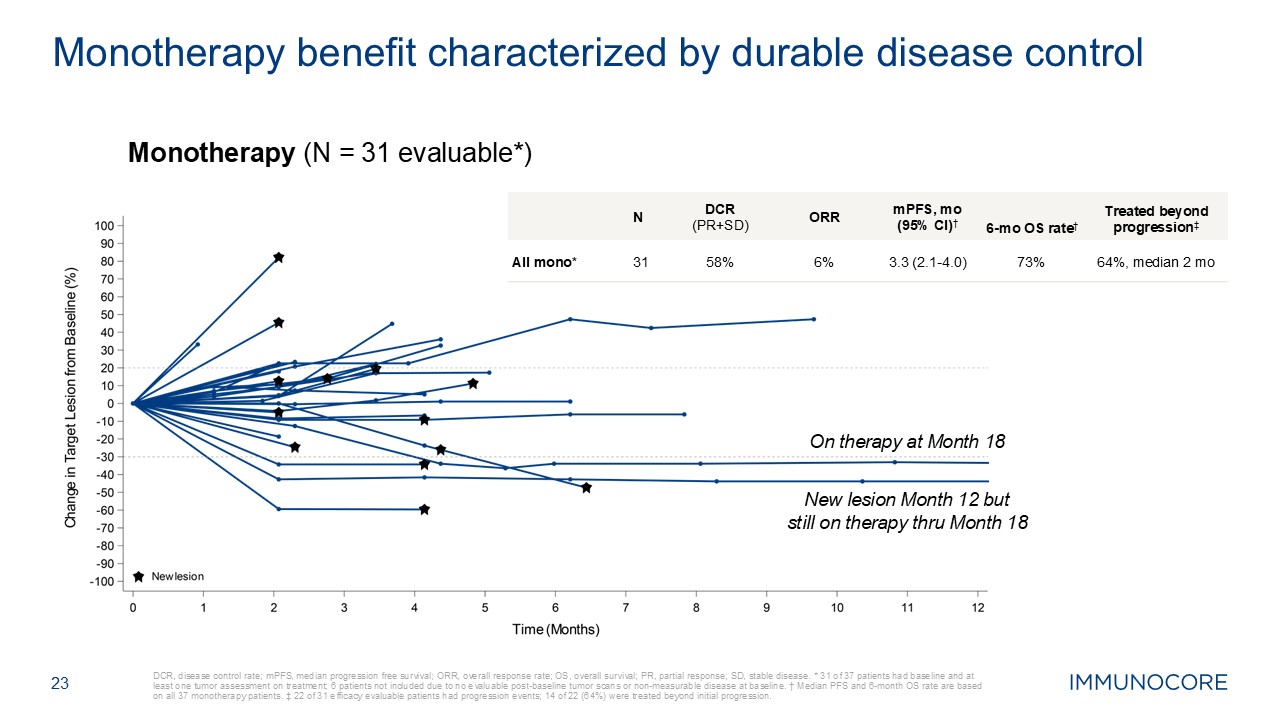
23 DCR, disease control rate; mPFS, median progression free survival; ORR,
overall response rate; OS, overall survival; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease. * 31 of 37 patients had baseline and at least one tumor assessment on treatment; 6 patients not included due to no evaluable post-baseline tumor scans or
non-measurable disease at baseline. † Median PFS and 6-month OS rate are based on all 37 monotherapy patients. ‡ 22 of 31 efficacy evaluable patients had progression events; 14 of 22 (64%) were treated beyond initial
progression. Monotherapy benefit characterized by durable disease control N DCR (PR+SD) ORR mPFS, mo (95% CI)† 6-mo OS rate† Treated beyond progression‡ All mono* 31 58% 6% 3.3 (2.1-4.0) 73% 64%, median 2 mo Monotherapy
(N = 31 evaluable*) On therapy at Month 18 New lesion Month 12 but still on therapy thru Month 18

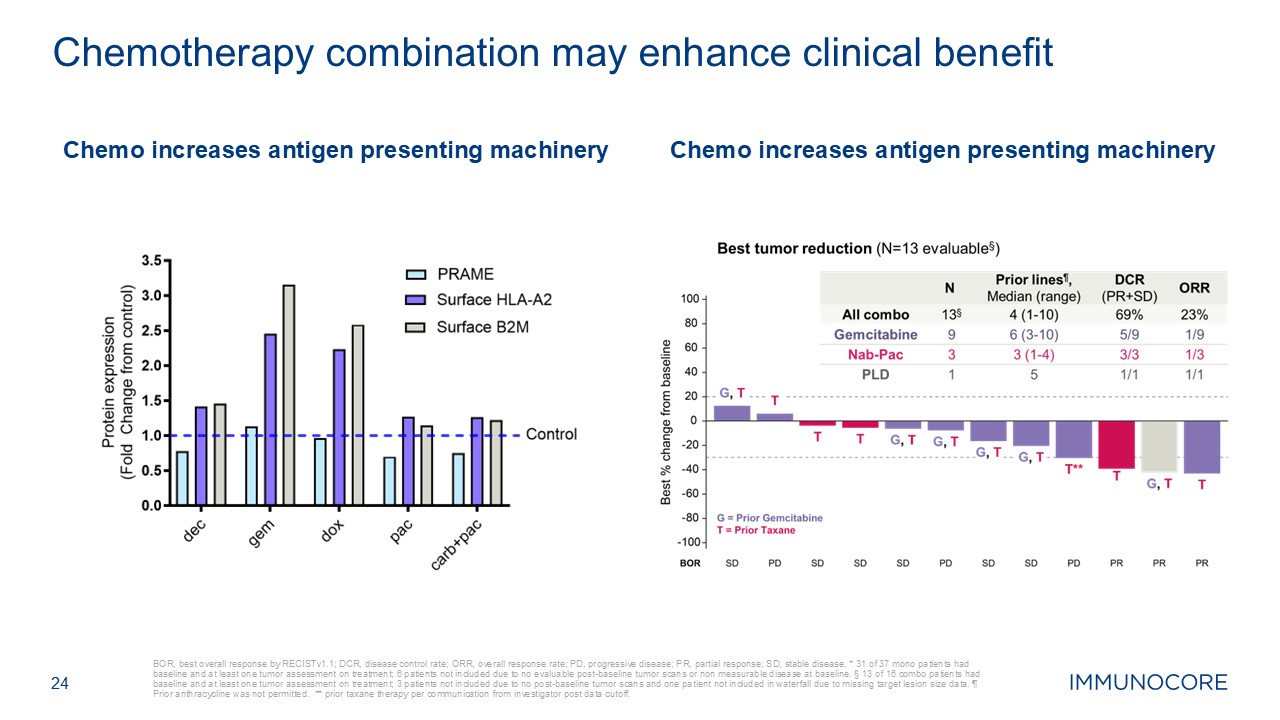
BOR, best overall response by RECISTv1.1; DCR, disease control rate; ORR,
overall response rate; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease. * 31 of 37 mono patients had baseline and at least one tumor assessment on treatment; 6 patients not included due to no evaluable post-baseline tumor
scans or non measurable disease at baseline. § 13 of 16 combo patients had baseline and at least one tumor assessment on treatment; 3 patients not included due to no post-baseline tumor scans and one patient not included in waterfall due to
missing target lesion size data. ¶ Prior anthracycline was not permitted. ** prior taxane therapy per communication from investigator post data cutoff. 24 Chemotherapy combination may enhance clinical benefit Chemo increases antigen
presenting machinery Chemo increases antigen presenting machinery

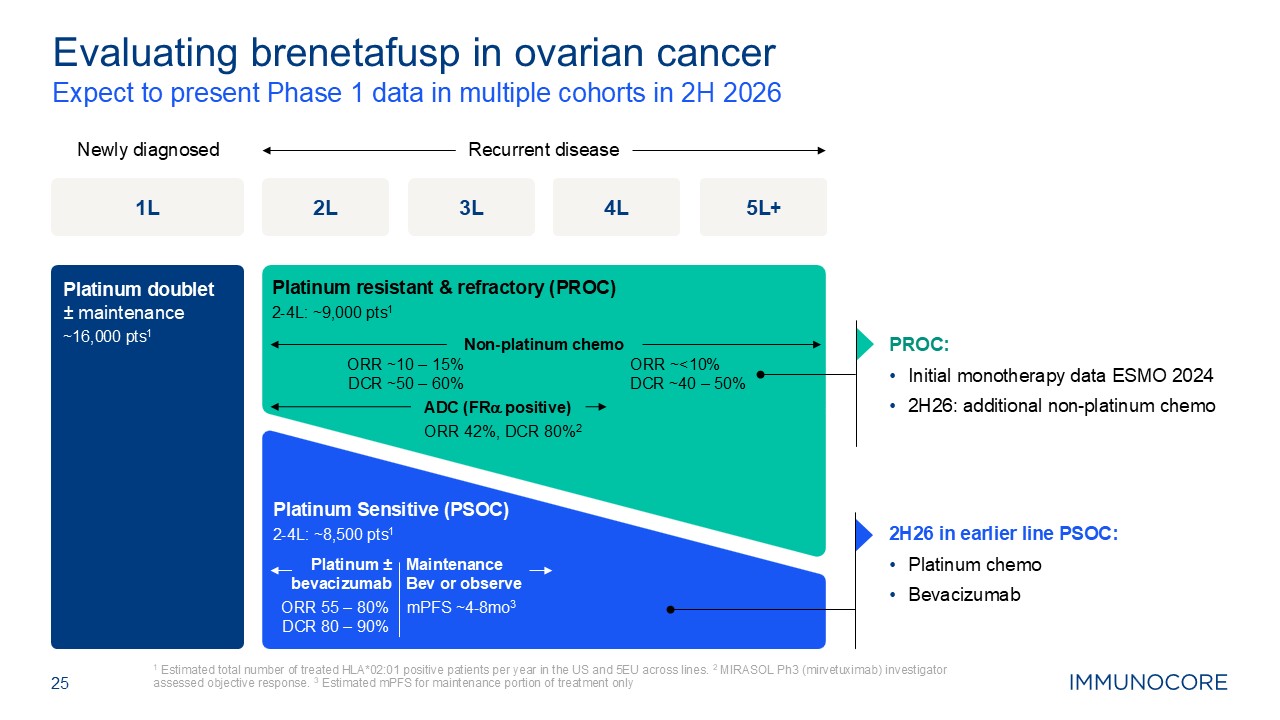
25 Expect to present Phase 1 data in multiple cohorts in 2H 2026 1 Estimated
total number of treated HLA*02:01 positive patients per year in the US and 5EU across lines. 2 MIRASOL Ph3 (mirvetuximab) investigator assessed objective response. 3 Estimated mPFS for maintenance portion of treatment only Evaluating
brenetafusp in ovarian cancer 1L 5L+ Recurrent disease Newly diagnosed Platinum doublet± maintenance ~16,000 pts1 2L 3L 4L PROC: Initial monotherapy data ESMO 2024 2H26: additional non-platinum chemo 2H26 in earlier line
PSOC: Platinum chemo Bevacizumab ORR 55 – 80% DCR 80 – 90% Maintenance Bev or observe ORR ~10 – 15% DCR ~50 – 60% Non-platinum chemo ORR ~<10% DCR ~40 – 50% Platinum ± bevacizumab mPFS ~4-8mo3 ADC (FRa positive) ORR
42%, DCR 80%2 Platinum Sensitive (PSOC) 2-4L: ~8,500 pts1 Platinum resistant & refractory (PROC) 2-4L: ~9,000 pts1

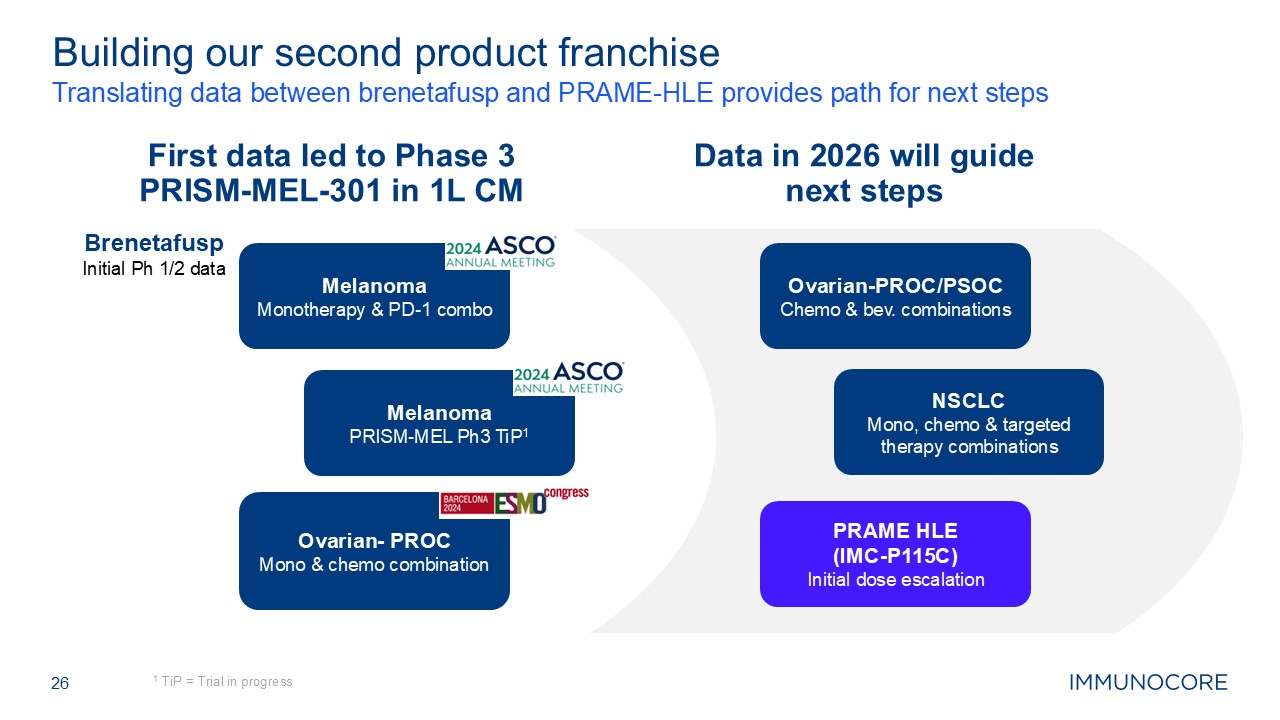
26 Translating data between brenetafusp and PRAME-HLE provides path for next
steps 1 TiP = Trial in progress Building our second product franchise First data led to Phase 3 PRISM-MEL-301 in 1L CM Brenetafusp Initial Ph 1/2 data Data in 2026 will guide next steps Melanoma Monotherapy & PD-1
combo Ovarian- PROC Mono & chemo combination Ovarian-PROC/PSOC Chemo & bev. combinations NSCLC Mono, chemo & targeted therapy combinations PRAME HLE (IMC-P115C) Initial dose escalation Melanoma PRISM-MEL Ph3 TiP1

Novel ImmTAC candidate for GI cancers from our discovery engine 27

~20K colorectal + ~15K other tumors2 patients positive for PIWIL1 and
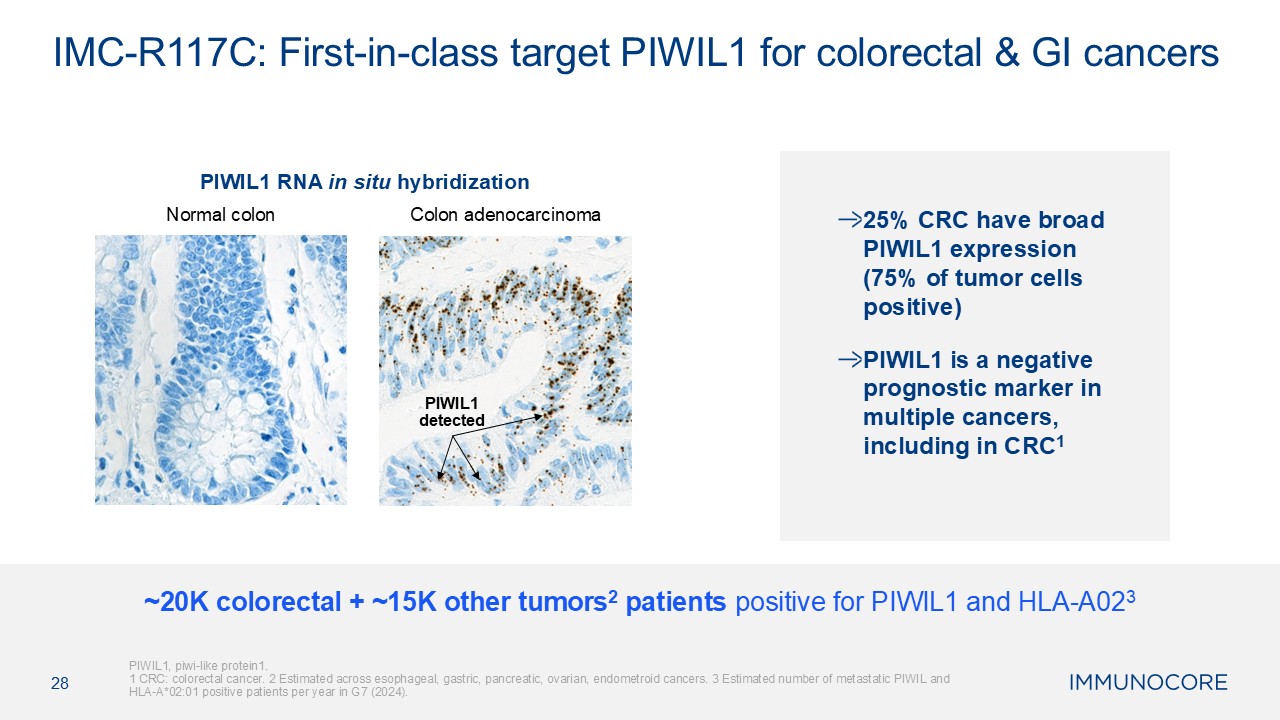
HLA-A023 28 IMC-R117C: First-in-class target PIWIL1 for colorectal & GI cancers Normal colon Colon adenocarcinoma PIWIL1 detected PIWIL1 RNA in situ hybridization 25% CRC have broad PIWIL1 expression (75% of tumor cells
positive) PIWIL1 is a negative prognostic marker in multiple cancers, including in CRC1 PIWIL1, piwi-like protein1. 1 CRC: colorectal cancer. 2 Estimated across esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, ovarian, endometroid cancers. 3 Estimated
number of metastatic PIWIL and HLA-A*02:01 positive patients per year in G7 (2024).

Pursuing a functional cure in infectious diseases 29

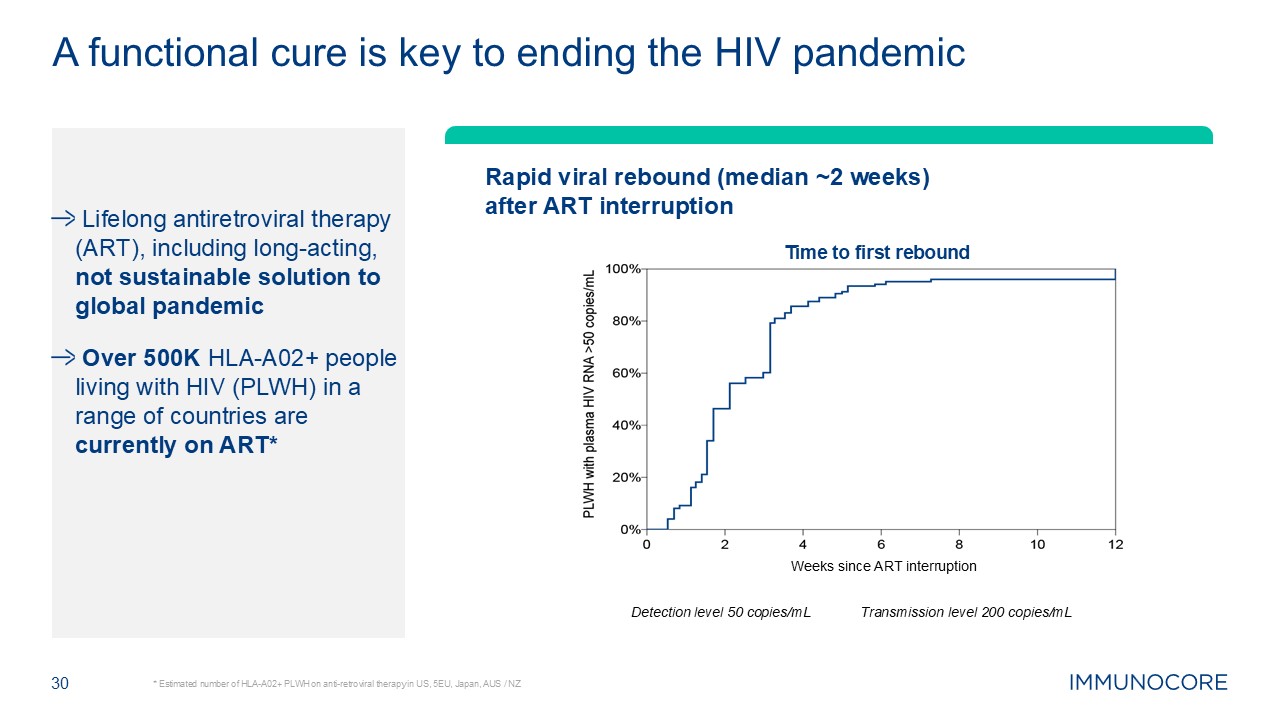
Lifelong antiretroviral therapy (ART), including long-acting, not
sustainable solution to global pandemic Over 500K HLA-A02+ people living with HIV (PLWH) in a range of countries are currently on ART* 30 * Estimated number of HLA-A02+ PLWH on anti-retroviral therapy in US, 5EU, Japan, AUS / NZ A
functional cure is key to ending the HIV pandemic Detection level 50 copies/mL Transmission level 200 copies/mL Rapid viral rebound (median ~2 weeks) after ART interruption Time to first rebound Weeks since ART interruption

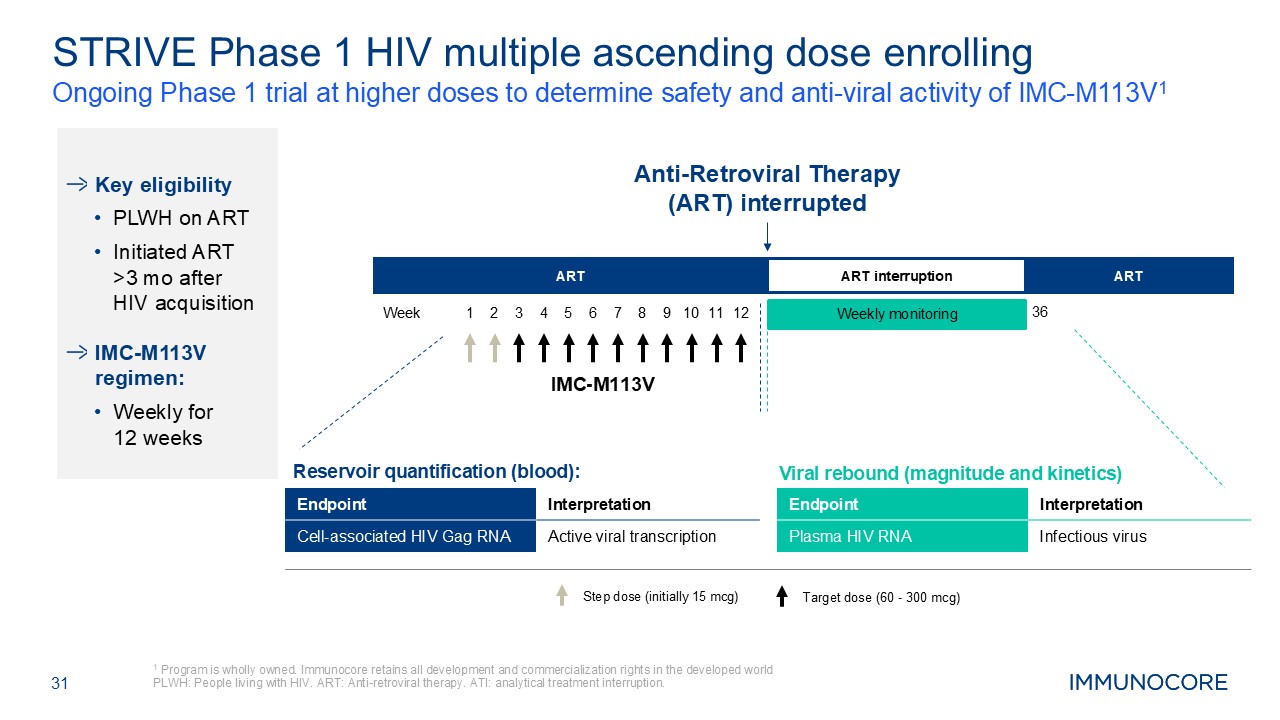
31 Ongoing Phase 1 trial at higher doses to determine safety and anti-viral
activity of IMC-M113V1 1 Program is wholly owned. Immunocore retains all development and commercialization rights in the developed world PLWH: People living with HIV. ART: Anti-retroviral therapy. ATI: analytical treatment
interruption. STRIVE Phase 1 HIV multiple ascending dose enrolling Key eligibility PLWH on ART Initiated ART >3 mo after HIV acquisition IMC-M113V regimen: Weekly for 12 weeks Endpoint Interpretation Cell-associated HIV Gag
RNA Active viral transcription Endpoint Interpretation Plasma HIV RNA Infectious virus Anti-Retroviral Therapy (ART) interrupted Step dose (initially 15 mcg) Target dose (60 - 300 mcg) Viral rebound (magnitude and
kinetics) Reservoir quantification (blood): IMC-M113V ART ART ART interruption Weekly monitoring Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 36

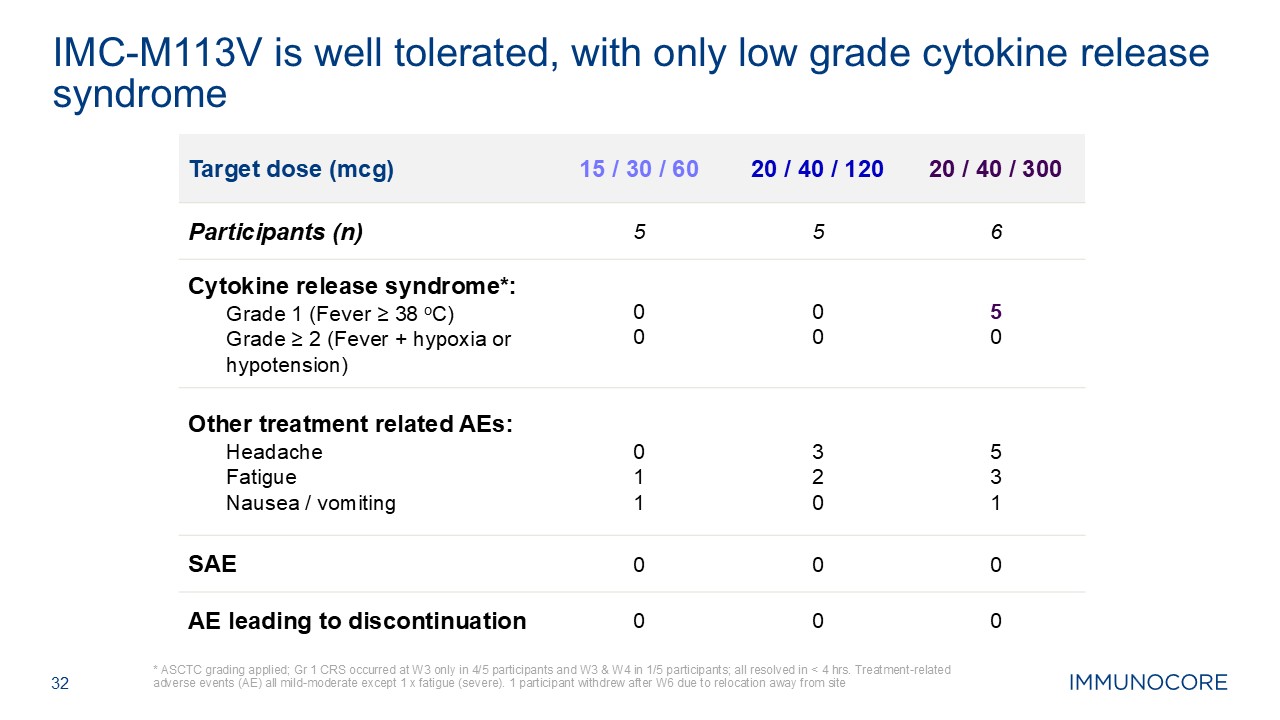
32 * ASCTC grading applied; Gr 1 CRS occurred at W3 only in 4/5 participants
and W3 & W4 in 1/5 participants; all resolved in < 4 hrs. Treatment-related adverse events (AE) all mild-moderate except 1 x fatigue (severe). 1 participant withdrew after W6 due to relocation away from site IMC-M113V is well
tolerated, with only low grade cytokine release syndrome Target dose (mcg) 15 / 30 / 60 20 / 40 / 120 20 / 40 / 300 Participants (n) 5 5 6 Cytokine release syndrome*: Grade 1 (Fever ≥ 38 oC) Grade ≥ 2 (Fever + hypoxia or
hypotension) 0 0 0 0 5 0 Other treatment related AEs: Headache Fatigue Nausea / vomiting 0 1 1 3 2 0 5 3 1 SAE 0 0 0 AE leading to discontinuation 0 0 0

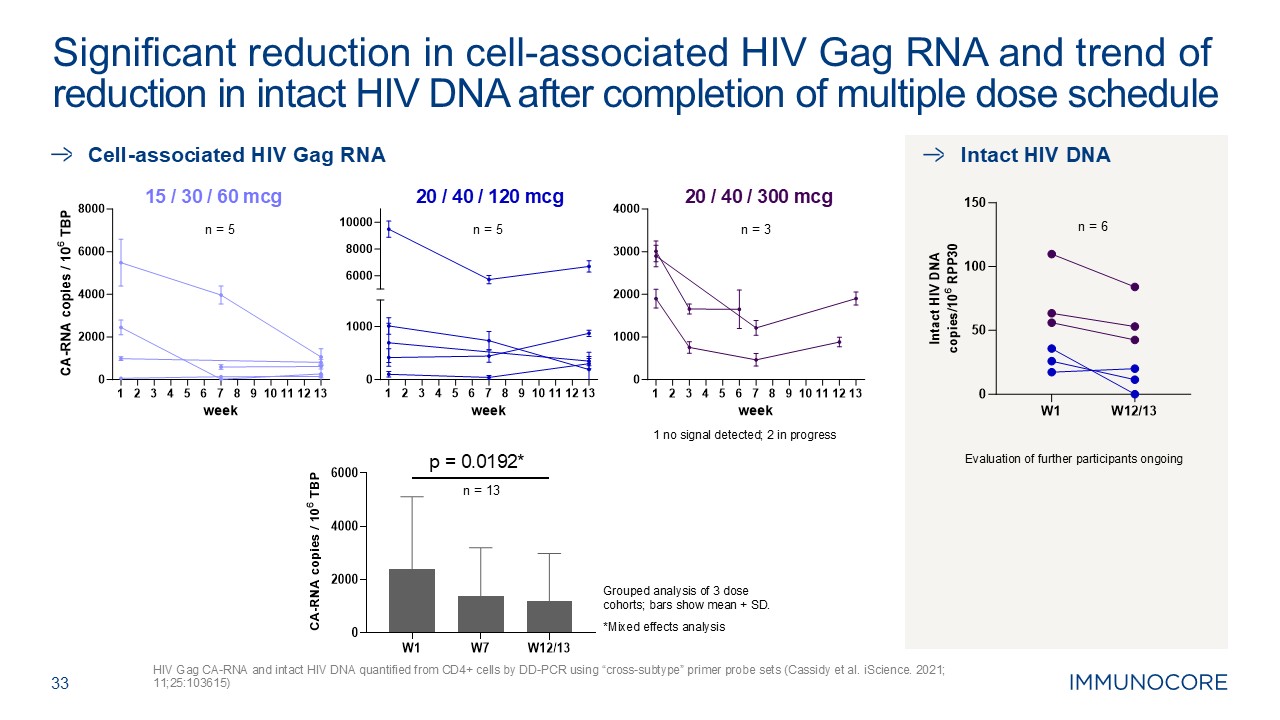
20 / 40 / 300 mcg 1 no signal detected; 2 in progress n = 3 20 / 40 / 120
mcg n = 5 33 HIV Gag CA-RNA and intact HIV DNA quantified from CD4+ cells by DD-PCR using “cross-subtype” primer probe sets (Cassidy et al. iScience. 2021; 11;25:103615) Significant reduction in cell-associated HIV Gag RNA and trend of
reduction in intact HIV DNA after completion of multiple dose schedule 15 / 30 / 60 mcg n = 5 p = 0.0192* n = 13 Grouped analysis of 3 dose cohorts; bars show mean + SD. *Mixed effects analysis n = 6 Cell-associated HIV Gag
RNA Intact HIV DNA Evaluation of further participants ongoing

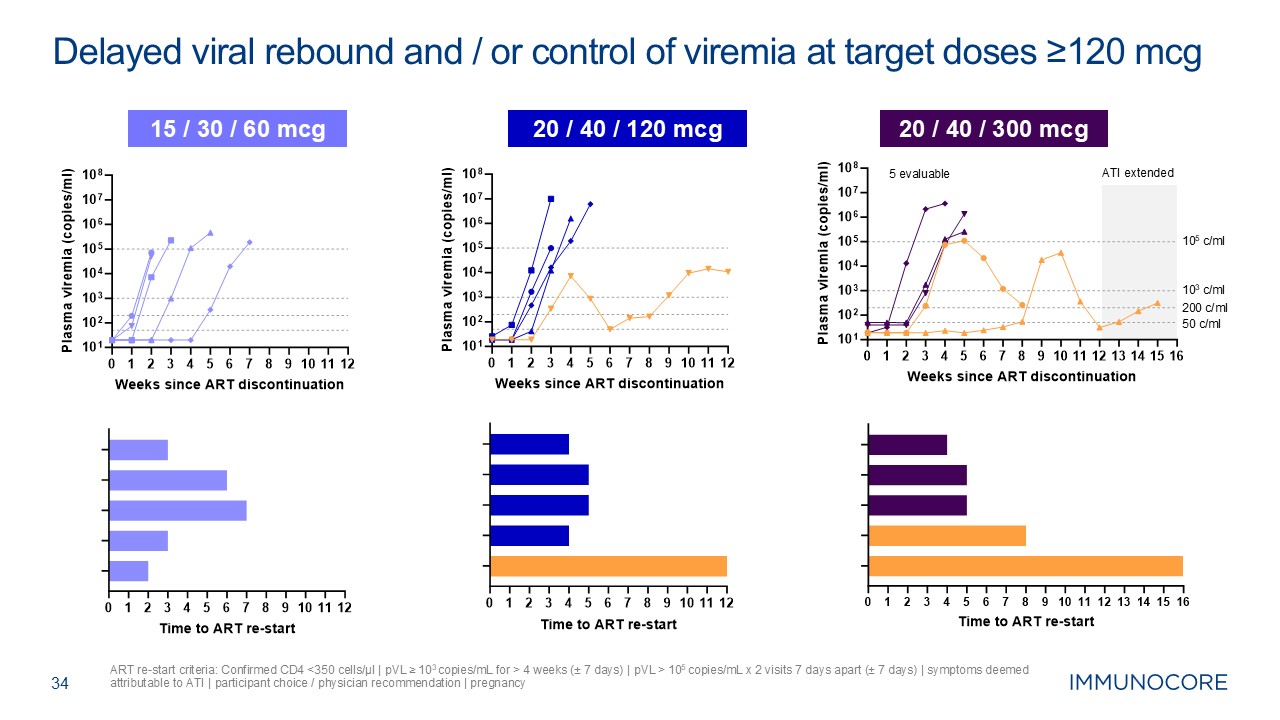
34 ART re-start criteria: Confirmed CD4 <350 cells/μl | pVL
≥ 103 copies/mL for > 4 weeks (± 7 days) | pVL > 105 copies/mL x 2 visits 7 days apart (± 7 days) | symptoms deemed attributable to ATI | participant choice / physician recommendation | pregnancy Delayed viral rebound and / or
control of viremia at target doses ≥120 mcg 15 / 30 / 60 mcg 20 / 40 / 120 mcg 20 / 40 / 300 mcg 5 evaluable 200 c/ml ATI extended 103 c/ml 105 c/ml 50 c/ml

Pioneering tissue-specific immune downmodulation for treatment of autoimmune
diseases 35

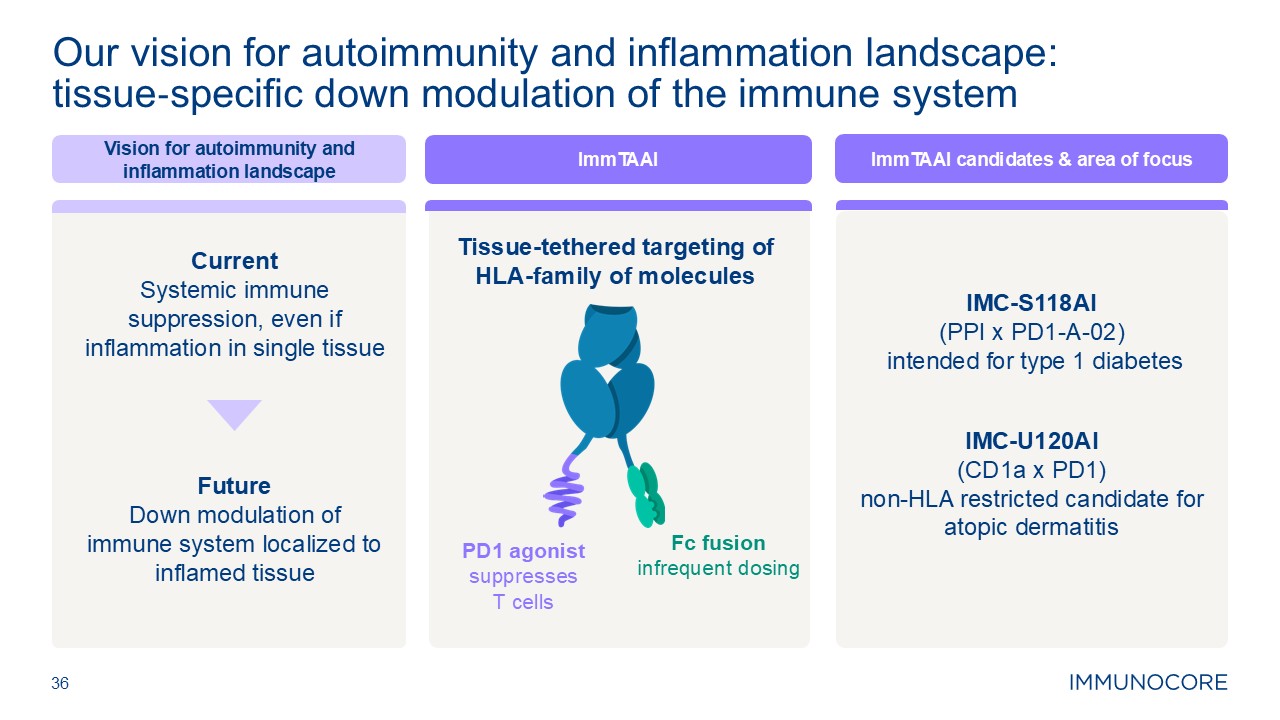
36 Our vision for autoimmunity and inflammation landscape: tissue‐specific
down modulation of the immune system Vision for autoimmunity and inflammation landscape Current Systemic immune suppression, even if inflammation in single tissue Future Down modulation of immune system localized to inflamed
tissue Tissue-tethered targeting of HLA-family of molecules PD1 agonist suppresses T cells Fc fusion infrequent dosing ImmTAAI ImmTAAI candidates & area of focus IMC-S118AI (PPI x PD1-A-02) intended for type 1 diabetes
IMC-U120AI (CD1a x PD1) non-HLA restricted candidate for atopic dermatitis

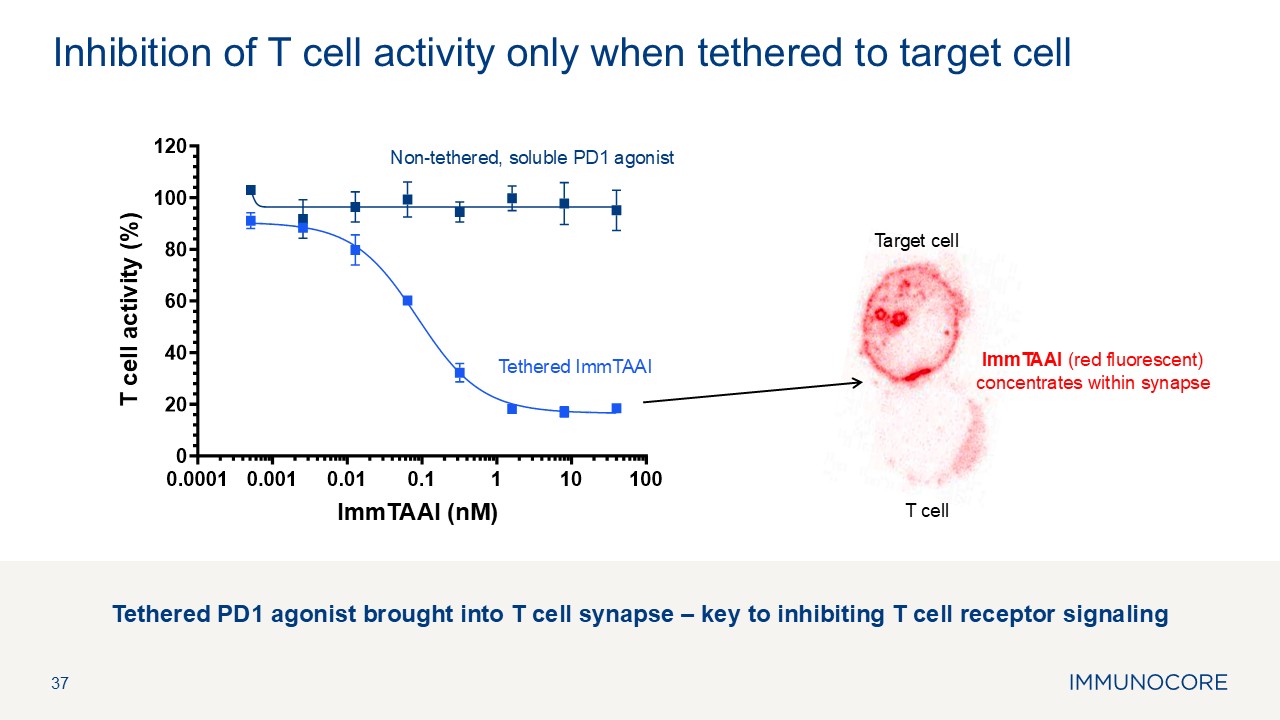
37 Inhibition of T cell activity only when tethered to target
cell Non-tethered, soluble PD1 agonist Tethered ImmTAAI ImmTAAI (nM) T cell activity (%) T cell Target cell Tethered PD1 agonist brought into T cell synapse – key to inhibiting T cell receptor signaling ImmTAAI (red fluorescent)
concentrates within synapse

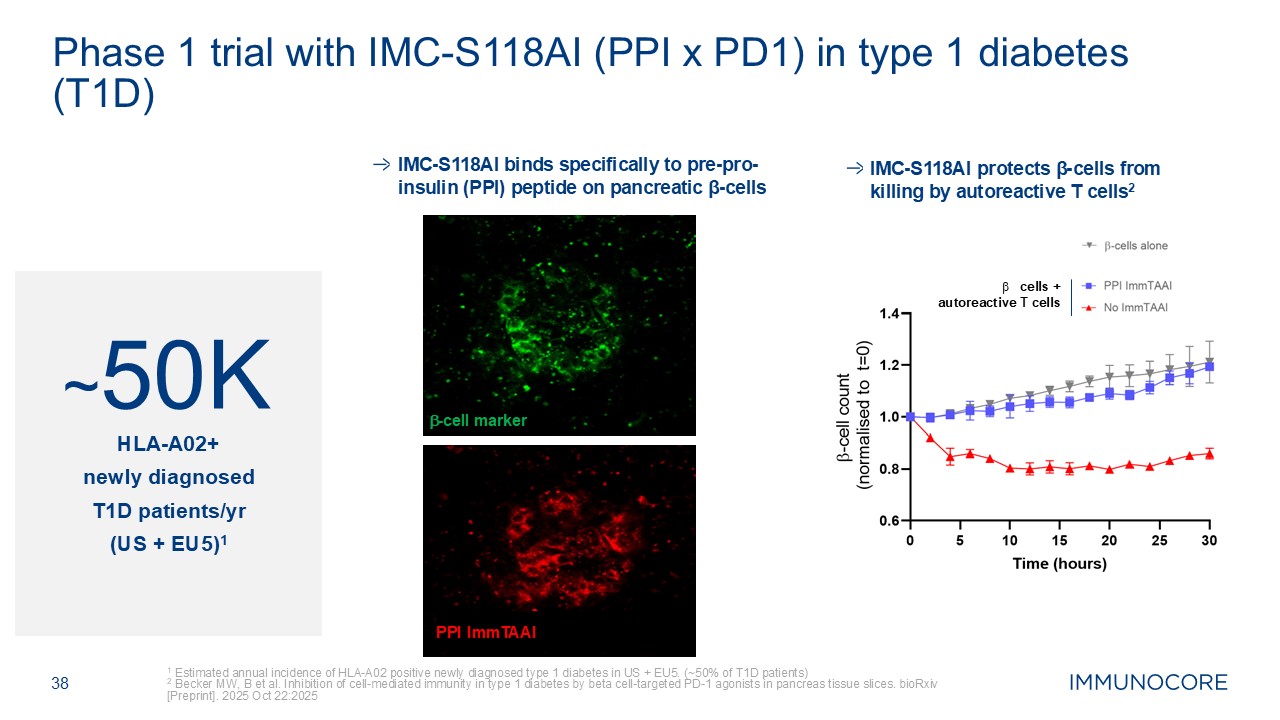
38 1 Estimated annual incidence of HLA-A02 positive newly diagnosed type 1
diabetes in US + EU5. (~50% of T1D patients) 2 Becker MW, B et al. Inhibition of cell-mediated immunity in type 1 diabetes by beta cell-targeted PD-1 agonists in pancreas tissue slices. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Oct 22:2025 Phase 1 trial
with IMC-S118AI (PPI x PD1) in type 1 diabetes (T1D) ~50K HLA-A02+ newly diagnosed T1D patients/yr (US + EU5)1 IMC-S118AI protects β-cells from killing by autoreactive T cells2 IMC-S118AI binds specifically to pre-pro-insulin
(PPI) peptide on pancreatic β-cells b-cell marker PPI ImmTAAI cells + autoreactive T cells

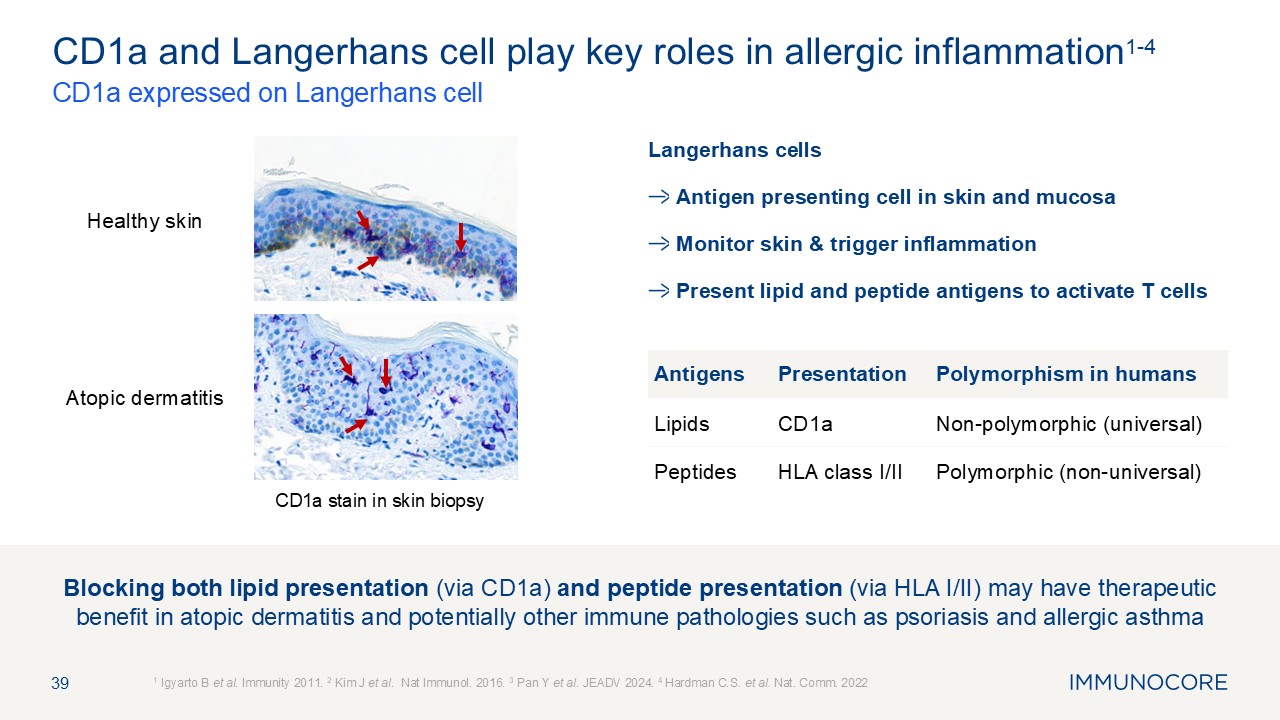
Blocking both lipid presentation (via CD1a) and peptide presentation (via HLA
I/II) may have therapeutic benefit in atopic dermatitis and potentially other immune pathologies such as psoriasis and allergic asthma 39 CD1a expressed on Langerhans cell 1 Igyarto B et al. Immunity 2011. 2 Kim J et al. Nat Immunol.
2016. 3 Pan Y et al. JEADV 2024. 4 Hardman C.S. et al. Nat. Comm. 2022 CD1a and Langerhans cell play key roles in allergic inflammation1-4 Langerhans cells Antigen presenting cell in skin and mucosa Monitor skin & trigger
inflammation Present lipid and peptide antigens to activate T cells CD1a stain in skin biopsy Antigens Presentation Polymorphism in humans Lipids CD1a Non-polymorphic (universal) Peptides HLA class I/II Polymorphic
(non-universal) Atopic dermatitis Healthy skin

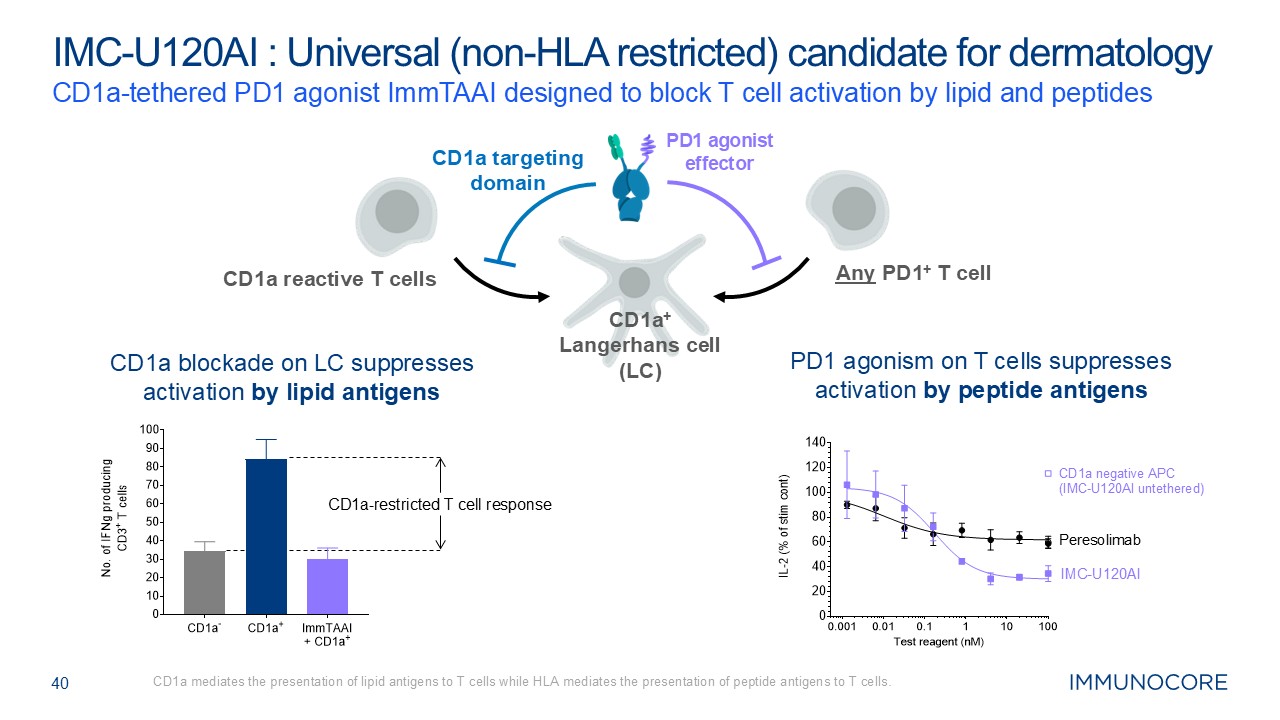
40 CD1a-tethered PD1 agonist ImmTAAI designed to block T cell activation by
lipid and peptides CD1a mediates the presentation of lipid antigens to T cells while HLA mediates the presentation of peptide antigens to T cells. IMC-U120AI : Universal (non-HLA restricted) candidate for dermatology CD1a+ Langerhans
cell (LC) CD1a targeting domain PD1 agonist effector CD1a blockade on LC suppresses activation by lipid antigens PD1 agonism on T cells suppresses activation by peptide antigens CD1a-restricted T cell response IMC-U120AI CD1a
negative APC (IMC-U120AI untethered) Peresolimab CD1a reactive T cells Any PD1+ T cell

Leading TCR pipeline 41

42 Registrational and proof of concept readouts throughout 2026 1Consists of
cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities. This amount is subject to change pending completion of the audited financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2025. Upcoming milestones Tebentafusp: Complete enrollment in Phase
3 trial (TEBE-AM) Autoimmune Diseases: First patient dosed in Phase 1 trial with IMC-S118AI in type 1 diabetes (T1D) 1H 2026 Tebentafusp: Earliest window for topline readout in Phase 3 trial (TEBE-AM) – event driven Brenetafusp: Data
from Phase 1/2 combinations in ovarian; including platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer Brenetafusp: Data from Phase 1/2 monotherapy and combinations in NSCLC PRAME-A02-HLE: Initial data from Phase 1 trial in multiple solid tumors Infectious
Diseases: Data from Phase 1 HIV trial Autoimmune Diseases: IND/CTA for CD1a x PD1 (non-HLA restricted) trial in atopic dermatitis 2H 2026 Complete registrational trials: PRISM-MEL-301 ATOM 2027+Milestones Additional programs –
PIWIL1, T1D, atopic dermatitis $864M preliminary & unaudited year end cash position1

Thank you 43